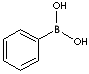
| BENZENEBORONIC ACID | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 98-80-6 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 202-701-9 | |
| FORMULA | C6H5B(OH)2 | |
| MOL WT. | 121.93 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
2931.00.3000 | |
|
TOXICITY |
Oral Rat LD50: 740mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | Acide phenylborique; Borophenylic acid; Dihydroxyphenylborane; | |
| Kyselina fenylborita; Phenylboric acid; Phenylboronic acid; Phenyldihydroxyborane; | ||
|
SMILES |
c1c(cccc1)B(O)O | |
CLASSIFICATION |
Boronic acid derivative, Cross coupling reagent |
|
|
EXTRA NOTES |
Boronic acid component in Suzuki bi-aryl cross-coupling | |
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white to off-white crystalline powder | |
| MELTING POINT |
216 - 219 C |
|
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | 4420 mg/l at 25 C | |
| SOLUBILITY IN SOLVENT | solubility in benzene : 1.75% xylene : 1.2 % methanol : 178 % ether : 30.2% | |
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
| pKa | 13.7 | |
| log Pow | (Octanol-water) | |
| VAPOR PRESSURE | 8.56E-06 (mmHg) | |
| HENRY'S LAW | (atm-m3/mole at 25 C) | |
| OH RATE | 2.23E-12 (cm3/molecule-sec at 25 C Atmospheric) | |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
| FLASH POINT |
|
|
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary conditions. |
|
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND EXTERNAL LINKS |
||
|
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phenylboronic_acid Material Safety Data Sheet: http://www.chemcas.com Phenylboronic acid, or benzeneboronic acid, is prepared by the reaction of the Grignard reagent PhMgBr with B(OMe)3. It and its aryl-substituted derivatives are commonly used as building blocks in synthetic organic chemistry—most often in the Suzuki coupling reaction, in which a boronic acid reacts with an organic halide to form a carbon–carbon bond. Boronic acids’ reactions with 1,2- and 1,3-diols are useful for saccharide recognition. http://portal.acs.org/Structurally, boronic acids are trivalent boron-containing organic compounds that possess one alkyl substituent (i.e., a C–B bond) and two hydroxyl groups to fill the remaining valences on the boron atom (Figure 1.1). With only six valence electrons and a consequent deficiency of two electrons, the sp2-hybridized boron atom possesses a vacant p orbital. This low-energy orbital is orthogonal to the three substituents, which are oriented in a trigonal planar geometry. Unlike carboxylic acids, their carbon analogues, boronic acids are not found in nature. These abiotic compounds are derived synthetically from primary sources of boron such as boric acid, which is made by the acidification of borax with carbon dioxide. Borate esters, the main precursors for boronic acid derivatives, are made by simple dehydration of boric acid with alcohols. The first preparation and isolation of a boronic acid was reported by Frankland in 1860 [1]. By treating diethylzinc with triethylborate, the highly air-sensitive triethylborane was obtained, and its slow oxidation in ambient air eventually provided ethylboronic acid. Boronic acids are the products of the second oxidation of boranes. Their stability to atmospheric oxidation is considerably superior to that of borinic acids, which result from the first oxidation of boranes. The product of a third oxidation of boranes, boric acid, is a very stable and a relatively benign compound to humans http://www.wiley-vch.de/
|
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white to off-white crystalline powder | |
|
ASSAY |
97.0% min | |
| MELTING POINT | 216 - 219 C |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING |
|
|
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 22-R36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 26-36/37/39 | ||