PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
Triphosgene; 1,1,1-Trichloromethanol 1,1'-carbonate; tri-Phosgene;
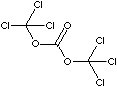
SMILES
CLASSIFICATION
Phosgene, Coupling reagent, Synthetic auxiliary, Peptide Synthesis
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
81 - 83 C
203 - 206 C
1.629
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS
Phosgene (carbonyl dichloride, COCl2) is a very reactive chemical intermediate to prepare isocyanates (from amines), chloroformates, isothiocyanates, isonitriles and acid chlorides (from carboxylic acids) as well as in the production of polymers including polyurethanes, polycarbonates, and polyureas. Phosgene , however, is extremely toxic gas associated strong safety hazards and handling precautions. It is listed on schedule 3 of the Chemical Weapons Convention. All production sites must be declared to the OPCW. Phosgene is almost entirely in captive consume in the production plant. Diphosgene, a liquid that can be handled safer relatively than phosgene, is a source of two equivalents of phosgene. It can convert amines into carbamates and alcohols into carbonates. Triphosgene is a safe and useful solid substitute for phosgene. 1 Mole corresponds in its reactivity to 3 moles phosgene. Some examples of Its use include Carboxylic acid to anhydride (Dehydration), Formide to isocyanide (Dehydration), Alcohol to alkyl halide (Halogenation), Carboxylic acid to acid halide (Halogenation), Epoxides to vicinal dichlorides (Halogenation), Amine to isocyanate and Alcohol to aldehyde (Oxidation), the one-pot preparation of allyl azides from allyl alcohols and sodium azide, the preparation of the esterification coupling reagent, di-2-thienyl carbonate, from 2(5H)-thiophenone. the preparation of 2-chloronicotinaldehydes via cyclization of the corresponding enamides.
Wikipedia
Linking:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosgene
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triphosgene
http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/
"Triphosgene
[bis(trichloromethyl) carbonate] is a stable, crystalline solid
which has proved to be a useful substitute for phosgene.1 It is
safer and more convenient to handle, transport and store. Exact
amounts may be weighed easily and used to perform desired chemical
transformations. Reaction requires only one-third equivalent of
triphosgene in most cases. Recently, triphosgene has been shown
to react with several alpha-amino acids to give the corresponding
N-carboxyanhydrides in good yields.....
http://www.bentham.org
The
use of triphosgene as a synthetic auxiliary in the preparation of
many important classes of organic compounds has been investigated
intensively in the last twenty years. This white crystalline compound
has proved as a safe and stable replacement of phosgene. Triphosgene
is known to react with carboxylic acids to produce carboxylic acid
chlorides or carboxylic acid anhydrides [5]. To the best of our
knowledge, no reports have yet appeared in the literature on the
conversion of carboxylic acids into Weinreb amides using triphosgene.
We wish to report herein a simple onepot procedure for the direct
conversion of carboxylic acids to Weinreb amides using triphosgene
as an acid activator as shown in Scheme 1........
APPEARANCE
79 - 83 C
ASSAY
99.0% min