|
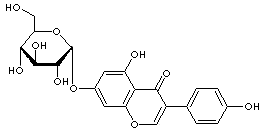
GENISTIN |
| Synonyms. Genistin; Genistein 7-glucoside; Genistein glucoside; Genistein 7-O-beta-D-glucoside; Genistein 7-beta-D-glucopyranoside; Genistein-7-glucoside; Genisteol 7-monoglucoside; Genistine; Genistoside; Glucopyranoside beta-D-genistein-7; Glucosyl-7-genistein; 4',5,7-Trihydroxyisoflavone 7-D-glucoside; 7-(beta-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
529-59-9 |
|
EINECS RN |
|
|
FORMULA |
C21H20O10 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
432.38 |
|
H.S CODE |
2938.90.0000 |
|
SMILES |
c1(c2c(cc(O[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@H]([C@H](O)[C@H](O3)CO)O)O) cc2O) occ 1c1ccc(O)cc1)=O |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Glycoside |
|
EXTRA NOTES |
Glycoside of soy bean isoflavone, gentistein. Selective inhibitor of mammalian terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT), with no measurable effect on mammalian or microbial DNA polymerases. |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE. |
white powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
254 C |
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
|
| SOLVENT SOLUBILITY | Soluble in acetone, poorly soluble in ethanol |
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
log P(octanol-water) |
|
|
VAPOR PRESSURE |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION TEMP |
|
| pH |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong Oxidizing agents |
| POLYMERIZATION |
Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health hazard: 1, Flammability: 0, Physical hazards: 0 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
|
Wikipedia Linking - Genistin Google Scholar Search - Genistin Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Genistin PubChem Compound Summary - Genistin Drug Bank - Genistin KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Genistin http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Genistin http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Genistin http://www.indjst.org/archive/ |
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
white to off-white powder |
|
ASSAY |
98.0% min |
| OPTICAL ROTATION |
-23° ~ -27° (c=0.6 in pyridine) |
| MELTING POINT |
244 - 255 C |
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
Not regulated |
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
|
| PACKING GROUP | |
|
|
| SAFETY INFORMATION |
|
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
Not known |
| HAZARD CODES |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
22-24/25 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
26-36 |
|
|