|
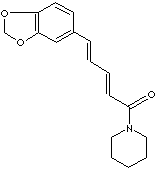
PIPERINE
|
| Synonyms. Piperine; 1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl-1-oxo-2,4-pentadienylpiperine; (E,E)-1-(5-(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-1-oxo-2,4-pentadienyl)piperidine; 1-Piperoylpiperidine; (E,E)-1-Piperoylpiperidine; Bioperine; Piperin; Piperoylpiperidine; (2E,4E)-5-(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-1-(1-piperidinyl)-2,4-pentadien-1-one; 1-((2E,4E)-5-(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-1-oxo-2,4-pentadienyl)piperidine; Other RN; 147030-08-8 |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
94-62-2 |
|
EINECS RN |
202-348-0 |
|
FORMULA |
C17H19NO3 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
285.34 |
|
H.S CODE |
2939.99.0000 |
|
SMILES |
c12c(ccc(c1)\C=C\C=C\C(N1CCCCC1)=O)OCO2 |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Alkaloid, Flavor |
|
EXTRA NOTES |
FEMA No. 2909 |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
off-white to yellow-tan crystalline powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
131 - 132 C |
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
40 mg/l |
| SOLVENT SOLUBILITY | Soluble in acetic acid, benzene, ethanol and chloroform. Slightly soluble in ether. |
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
VAPOR PRESSURE |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION TEMP |
|
| pH |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
|
STABILITY AND REACTIVITY |
|
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon oxides. |
| POLYMERIZATION |
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health Hazard: 1, Fire: 2, Reactivity Hazard: 0 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
|
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Piperine PubChem Compound Summary - Piperine KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Piperine http://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/ - Piperine http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Piperine http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/ http://www.britannica.com/ http://aac.asm.org/ |
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
off-white to yellow-tan crystalline powder |
|
PURITY |
98.0% min |
|
HEAVY METALS |
10ppm max |
|
MELTING POINT |
128 - 132 C |
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
Not regulated |
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
|
| PACKING GROUP | |
|
|
| SAFETY INFORMATION |
|
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
Harmful by ingestion. This substance has caused adverse reproductive and fetal effects in animals. |
|
GHS |
|
|
SIGNAL WORD |
Warning |
|
PICTOGRAMS |
|
|
HAZARD STATEMENTS |
H302 H312 |
|
P STATEMENTS |
P280 P302+P352 H312 |
| EC DIRECTIVES |
|
| HAZARD CODES |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
21/22 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
36/37 |
|
|
| PACKING |
|
|
|
|
|
|