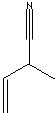
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
0.81
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
15 C
APPLICATIONS
Although nitriles don't have a carbonyl group, they are often considered as derivatives of carboxylic acids. Nitrile undergoes acid hydrolysis to form a carboxylic acid. Nitrile is reduced to form amine in the presence of nickel catalyst. Grignard reagents add to nitriles, forming a relatively stable imino derivative which can be hydrolyzed to a ketone. Metaloimine is hydrolyzed to give beta-ketoester. Nitrile undergoes a sequence of nucleophilic additions with an alcohol under acid catalysis, called nitrile alcoholysis. Nitriles are hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids, alcoholyzed to esters, reduction to amines, cyclized to pyridine derivatives.
2-Methyl-3-butenenitrile finds applications in dye and flavour & fragrance manufacturing, rubber chemicals, and lubricant as well as a monomer.APPEARANCE
CONTENT
85.0% min
4.0% max
10.0% max
MOISTURE
0.2% max
3
1993
Hazard Symbols: F XN, Risk Phrases: 11-20/22, Safety Phrases: 16-23