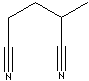
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
0.95
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
126 C
APPLICATIONS
Nitrile is an organic compounds containing cyano group (-C��N, containing trivalent nitrogen) which is attached to one carbon atom with the general formula RC��N. Their names are corresponding to carboxylic acids by changing '-ic acid' to the suffix, '-onitrile' which denotes only the ��N atom (triply bound) excluding the carbon atom attached to it, or the suffix, '-carbonitrile' where the carbon atom in the -CN is included, whichever preserves a single letter O. Examples are acetonitrile from acetic acid and benzonitrile from benzoic acid. The prefix, 'cyano-' is used as an alternative naming system to indicate the presence of a nitrile group in a molecule for the compounds of salts and organic derivatives of hydrogen cyanide (HC��N). Isocyanides are salts and hydrocarbyl derivatives from the isomer, HN+��C-. Sodium cyanide, NaCN; potassium cyanide, KCN; calcium cyanide, Ca(CN)2; and hydrocyanic (or prussic) acid, HCN are examples. Chemically, the simple inorganic cyanides resemble chlorides in many ways. Organic nitriles act as solvents and are reacted further for various application including;
·
Extraction solvent for fatty acids,
oils and unsaturated hydrocarbons
· Solvent for spinning and casting and
extractive distillation based on its selective miscibility with organic
compounds.
· Removing agent of colouring matters and aromatic
alcohols
· Non-aqueous solvent for titrations and for inorganic
salts
· Recrystallization of steroids
·
Parent compound for organic
synthesis
· Solvent or chemical intermediate in biochemistry ( pesticide
sequencing and DNA synthesis)
·
High-pressure liquid chromatographic
analysis
· Catalyst and component of transition-metal complex
catalysts
· Stabilizer for chlorinated
solvents
· Chemical intermediate and solvent for perfumes and
pharmaceuticals
Although nitriles don't have a carbonyl group, they are often considered as derivatives of carboxylic acids. Nitrile undergoes acid hydrolysis to form a carboxylic acid. Nitrile is reduced to form amine in the presence of nickel catalyst. Grignard reagents add to nitriles, forming a relatively stable imino derivative which can be hydrolyzed to a ketone. Metaloimine is hydrolyzed to give beta-ketoester. Nitrile undergoes a sequence of nucleophilic additions with an alcohol under acid catalysis, called nitrile alcoholysis. Nitriles are hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids, alcoholyzed to esters, reduction to amines, cyclizized to pyridine derivatives.
APPEARANCE
CONTENT
99.5% min
30ppm max
0.3% max
0.5% max
6.1
2810