| 4,4'-AZOBIS(4-CYANOVALERIC ACID) | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 2638-94-0 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 220-135-0 | |
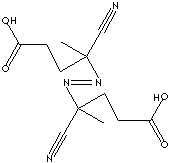
| FORMULA | [=NC(CH3)(CN)CH2CH2CO2H]2 | |
| MOL WT. | 280.28 | |
| H.S. CODE | ||
| TOXICITY | ||
| SYNONYMS | 4,4'-Azobis-4-cyanovaleric acid; | |
| cis-4,4'-Azobis(4-cyanovaleric acid); | ||
| 4,4'-azobis[4-cyano-Pentanoic acid; Azobis(cyanovaleric acid); 4,4'-azobis(4- cyano-Valeric acid; Kyselina 4,4'-azo-bis-(4-kyanvalerova); 4,4-Azobis-4-cyano Valeric acid; | ||
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white powder | |
| MELTING POINT | 110 - 120 C (Decomposes) | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
| |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Solublle | |
| AUTOIGNITION | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| FLASH POINT | ||
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
Polymerization
is initiated generally by free radical. There are four types of free radical
initiators which initiate polymerization.
Some Azocompound initiators include:
4,4'-Azobis(4-cyanovaleric acid) is as an initiator of free radical reactions for the production of polymer (polyvinyl chloride, polyacrylonitrile, polyvinyl alcohol and synthetic fibers) and as a blowing agent for plastics and elastomers. It is soluble in water. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white crystal | |
| PURITY |
98.0% (Dry basis) | |
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
30 - 50% | |
|
IRON |
10ppm max | |
|
HEAVY METAL |
10ppm max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 120kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 4.1 (Packing Group: II) | |
| UN NO. | 1325 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| half live at 69 C: 10 hrs (water) | ||
| DESCRIPTION OF BLOWING AGENT | ||
|
Blowing agents, also called Foaming agents, can be classified as Physical and Chemical Blowing Agents. Physical blowing agents are not under chemical changes during processing. Physical blowing agents are in forms of liquid or compressed gas which will transfer state into gases or low boiling liquid during processing causing resins into cellular structure. Chemical Blowing Agents are mainly solid form of hydrazine derivatives include Azodicarbonamide; p,p'-Oxybis(benzenesulfonyl hydrazide); 5-Phenyltetrazole; p-Toluene sulfonyl semicarbazide; Trihydrazine Triazine; They commonly release gases such as nitrogen, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide or ammonia. But ammonia is not desirable as it effects on degrade of resins. There are nonazo blowing agents releasing carbon dioxide such as sodium borohydride. |
||