PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
Natural occurrence: Vanilla, fennel, star anise, cranberry, black currant, cinnamon, basil.
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
clear to slight yellow liquid
MELTING POINT
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
AUTOIGNITION
225 C
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
116 C
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - p-Anisaldehyde
PubChem Compound Summary - p-Anisaldehyde
IPCS INCHEM - p-Anisaldehyde
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - p-Anisaldehyde
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - p-Anisaldehyde
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - p-Anisaldehyde
http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/
Hazardous
Substances Data Bank - p-Anisaldehyde
Local:
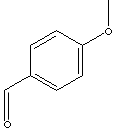
Anisole is one of the simplest aromatic compound to which ether group is linked. But it is different with aromatic compounds like furan where the oxygen is a part of the ring. Anisole, C6H5OCH3 (methyl phenyl ether), is a clear liquid that is soluble in ether and alcohol insoluble in water boiling point 155 C. Anisole and its derivatives are used as solvents and in perfumery. Anisole can be obtained from anise seed. Anisic acid, p-methoxybenzoic acid, is a part of cresol class antiseptic compounds. It is also used as an insect repellent and ovicide. Anisole, anisic acid, and their derivatives are also widely used in chemical reaction as intermediates to obtain target materials such as dyes, pharmaceuticals, perfumes, photoinitiators and agrochemicals. p-Anisaldehyde, an aromatic aldehyde with mothoxy gruop, is a clear liquid may discolor to yellow on storage (limited shelf life for 6 months) melting at -1 C, boiling at 249.5 C insoluble in water, soluble in alcohol and ether. It is used in the synthesis of other organic compounds including pharmaceuticals (especially antihistamines), agrochemicals, dyes and plastic additives. It is an important intermediate for the processing of perfumes and flavouring compounds.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF BENZALDEHYDE: Benzaldehyde(also called Benzenecarbonal) is the simplest representative of the aromatic aldehydes. It is a colorless liquid aldehyde with a characteristic almond odor. It boils at 180° C, is soluble in ethanol, but is insoluble in water.Benzaldehyde is formed by partial oxidation of benzyl alcohol and readily oxidized to benzoic acid and is converted to addition products by hydrocyanic acid or sodium bisulfite. It is also prepared by oxidation of toluene or benzyl chloride or by treating benzal chloride with an alkali, e.g., sodium hydroxide. It is used chiefly in the synthesis of other organic compounds, ranging from pharmaceuticals to plastic additives and benzaldehyde is an important intermediate for the processing of perfume and flavouring compounds and in the preparation of certain aniline dyes It is the first step in the synthesis for fragrances. It undergoessimultaneous oxidation and reduction with alcoholic potassium hydroxide, giving potassium benzoate and benzyl alcohol. It is converted to benzoin with alcoholic potassium cyanide, with anhydrous sodium acetate and acetic anhydride, giving cinnamic acid. Compounds which do not have alpha-hydrogen atoms cannot form an enolate ion and do not undergo electrophilic alpha-substitution and aldol condensation. Aromatic aldehydes such as benzaldehyde and formaldehyde may undergo disproportionation in concentrated alkali (Cannizaro's reaction) one molecule of the aldehyde is reduced to the corresponding alcohol and another molecule is simultaneously oxidized to the salt of a carboxylic acid. The speed of the reaction depends on the substituents in the aromatic ring. Two different types of aldehydes (aromatic and aliphatic) can undergo crossing reaction to form fomaldehyde and aromatic alcohols.
APPEARANCE
99.0% min
0.5% max
20ppm max
0.1% max
Not regulated
HAZARD OVERVIEW
May cause respiratory tract irritation. Harmful if swallowed. Causes eye and skin irritation. Target Organs: Blood, kidneys, central nervous system, liver, eyes, skin.
GHS
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H302
P STATEMENTS
P301 + P330 + P331
![]()
RISK PHRASES
36 Irritating to eyes
43 May cause sensitisation
by skin contact
SAFETY PHRASES
24 Avoid contact with skin
PRICE INFORMATION