PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
white crystals
REFRACTIVE INDEX
142 C
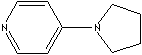
Pyridine and its derivatives are very important in industrial field as well as in bio chemistry. Nucleotide consist of either a nitrogenous heterocyclic base (purine or pyrimidine). Three major pyrimidines in living systems are cytosine, thymine, and uracil. Pyrimidine and its derivatives are biologically important components of nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) and coenzymes. Some pyridine system is active in the metabolism in the body. They can be the parent compound of many drugs, including the barbiturates. Pyridine and its derivatives are used as solvents and starting material for the synthesis of target compounds such as insecticides, herbicides, medicines, vitamins, food flavorings, feed additives, dyes, rubber chemicals, explosives, disinfectants, and adhesives. Pyridine is also used as a denaturant for antifreeze mixtures, as a dyeing assistant in textiles and in fungicides. 4-Pyrrolidinopyridine is used as a catalyst for the production of polyurethane and polyester. It is known to be the most effective catalyst for the acylation of alcohols. Nitrogen in pyridine involves in the introduction of sterically demanding asymmetric center to achieve effective stereocontrol.
APPEARANCE
white crystals
ESTER CONTENT
99.0% max
OTHER INFORMATION