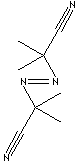| AZOBISISOBUTYRONITRILE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 78-67-1 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 201-132-3 | |
| FORMULA | (CH3)2C(CN)N=NC(CH3)2CN | |
| MOL WT. | 164.21 | |
| H.S. CODE | 2927.00 | |
| TOXICITY | Oral rat LD50: 100 mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | 2,2'-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile); | |
| 2,2'-Azobis[2-methylpropanenitrile]; AIBN; alpha,alpha'-Azodiisobutyronitrile; 2,2'-Dicyano-2,2'-azopropane; 2,2'-azo-bis(isobutyronitrile); 2,2'-Dimethyl-2,2'- azodipropionitrile; Azodiisobutyrodinitrile; 2,2[-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile); | ||
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white to off-white powder | |
| MELTING POINT | Decomposes | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.1 |
|
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Insoluble (Soluble in alcohol) | |
| AUTOIGNITION | 64 C | |
| VAPOR DENSITY | 5.7 | |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
|
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
| FLASH POINT |
|
|
| STABILITY | Unstable (shock sensitive, explosive decomposition by acetone, thermally unstable) | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| Azo is the
prefix for the group -N=N- or a combining form of azote which share the
core azobenzene structure. Azo compounds have a general
molecular formula of R-N=N-R', where R is aryl,
heteroaryl, -CH=C(OH)- or aliphatic. The extended delocalization of
electrons in the benzene and azo groups forms a conjugated system absorbing
visible frequencies of light. Aromatic groups provide characteristic colors of
red, orange, and yellow. This is the fundamental structure
of azo dyes. Aliphatic azo compounds are unstable and
the loss of nitrogen gas occurs by the simultaneous
cleavage of carbon-nitrogen bonds, resulting in carbon-centered
radicals. some aliphatic azo compounds are utilized as radical initiators. Azobisisobutyronitrile
is used as an initiator of free radical reactions for
the production of polymer (polyvinyl chloride, polyacrylonitrile,
polyvinyl alcohol and synthetic fibers) and as a blowing
agent for plastics and elastomers. Some Azocompound initiators include:
|
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white to off-white crystal or crystalline powder | |
| PURITY |
98.0% min |
|
|
INSOLUBLES |
0.01% max (in EtOH) |
|
|
VOLATILES |
1.0% max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 20kgs in bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 4.1 | |
| UN NO. | 3242 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
|
Nitrile is an organic compounds containing cyano group (-C��N, containing
trivalent nitrogen) which is attached to one carbon atom with the general
formula RC��N. Their names are corresponding to carboxylic acids by changing '-ic
acid' to the suffix, '-onitrile' which denotes only the ��N atom (triply bound)
excluding the carbon atom attached to it, or the suffix, '-carbonitrile' where
the carbon atom in the -CN is included, whichever preserves a single letter O.
Examples are acetonitrile from acetic acid and benzonitrile from benzoic acid.
The prefix, 'cyano-' is used as an alternative naming system to indicate the
presence of a nitrile group in a molecule for the compounds of salts and
organic derivatives of hydrogen cyanide (HC��N). Isocyanides are salts and hydrocarbyl
derivatives from the isomer, HN+��C-.
Sodium cyanide, NaCN; potassium
cyanide, KCN; calcium cyanide, Ca(CN)2; and hydrocyanic (or prussic) acid, HCN
are examples. Chemically, the simple inorganic cyanides resemble chlorides in
many ways. Organic nitriles act as solvents and are reacted further for various application including;
·
Extraction solvent for fatty acids,
oils and unsaturated hydrocarbons |
||