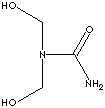
| (Hydroxymethyl)-Urea
and Bis(hydroxymethyl)-Urea are used as disinfectants,
slimicide or algaecides for air, materials and equipment,
whereas are not used for direct food or food contacts.
Dimethylolurea is used in animal feeds to keep feed
protein quality as it modifies tyrosine residues by
decreasing microbial degradation. They are used as a
preservative in metal-working fluids and processing
systems. They are used to treat plywoods to increase
hardness and fire resistance, and to form self-binding
laminations and to treat textiles for better stiffness,
shrink-resistannce for cottons, finishing, drying, sizing,
and tanning. They are used as photographic film developers.
They are used as intermediate for crosslinking agents
for polymers and coatings. |