CHELATING AGENTS
GENERAL
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
DTPA ACID
EDTA ACID
NTA ACID
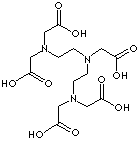
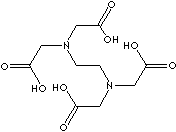
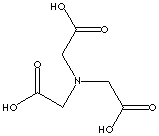
CAS NO.:
67-43-6
FORMULA:
C14H23N3O10
MOL WT.:
393.35
CAS NO.:
60-00-4
FORMULA:
C10H16O8N
MOL WT.:
292.25
CAS NO.:139-13-9
FORMULA:
C6H9NO6
MOL WT.:
191.14
Photography, Detergent, Chemical plating, Electroplating without cyanide, cleaning agent, plastic additives, printing of cotton and chemical fiber, industrial desulfation, inhibitor for plant growth, printing ink, medicine, paper and food industry. Water treatment chemical, Agriculture
SPECIFICATION
|
PROPERTY |
DTPA |
EDTA |
NTA |
|
Appearance |
White powder |
White powder |
White to
off-white |
|
Assay |
99 wt% min as H5 DPTA |
99 wt% as H4 EDTA |
98 wt% min as H3 NTA |
|
Chelation Value |
2.5 mmol/g |
3.39 mmol/g |
5.2 mmol/g |
|
pH |
2.1-2.5 (saturated sol.) |
2.5-3.0 (saturated sol.) |
1.7-2.7 (1% aqueous sol.) |
|
Water Solubility |
0.5 wt% max at 25°C |
0.1 wt% max at 25°C |
0.15 wt% max at 25°C |
SYNONYMS
Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid; Diethylenetriamine-N,N,N',N',N''-pentaacetic acid; Pentetic acid; N,N-Bis(2-(bis-(carboxymethyl)amino)ethyl)-glycine; Diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid, [[(Carboxymethyl)imino]bis(ethylenenitrilo)]-tetra-acetic acid
EDTA:
Edetic acid; Ethylenedinitrilotetraacetic acid; EDTA, free base; EDTA free acid; Ethylenediamine-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid; Hampene; Versene; N,N'-1,2-Ethane diylbis-(N-(carboxymethyl)glycine); ETHYLENEDIAMINE TETRA-ACETIC ACID
NTA:
N,N-bis(carboxymethyl)glycine; Triglycollamic acid; Trilone A; alpha,alpha',alpha''-trimethylaminetricarboxylic acid; Tri(carboxymethyl)amine; Aminotriacetic acid; Hampshire NTA acid; nitrilo-2,2',2''-triacetic acid; Titriplex i; Nitrilotriacetic acid
CHELATING
AGENTS