PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
Aldehyde, Flavor, Fungicide
EXTRA NOTES
EPA Pesticide Chemical Code 040506
FEMA No. 2286
Flavis number 5.014
A flavoring agent; an antimutagen but recent studies showed that high doses of cinnamaldehyde in the liver may produce a clastogenic and possibly a promoting effect for hepatocarcinogenesis.
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
MELTING POINT
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
AUTOIGNITION
REFRACTIVE INDEX
71 C
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Cinnamaldehyde
PubChem Compound Summary - Cinnamaldehyde
IPCS INCHEM - Cinnamaldehyde
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Cinnamaldehyde
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Cinnamaldehyde
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Cinnamaldehyde
http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/
Hazardous
Substances Data Bank - Cinnamaldehyde
Local:
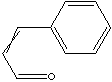
Cinnamic aldehyde is a oily yellow liquid with strong odor of cinnamon. This compound is the main component of cinnamon oil, a volatile oil used as a flavoring agent for pharmaceuticals. Cinnamaldehyde is obtained from the distillation with steam from the leaves and twigs of Cinnamomum. It can be
prepared from the synthesis from related compounds like cinnamyl alcohol and from the condensation of benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde. Cinnamic aldehyde is a benzene ring substituent acrylic aldehyde having carbon-carbon solid bond. The conjugated solid bond makes geometry of the compound planar. Though there are cis and trans isomers, cinnamic aldehyde usually refers to the latter which the terminal carbonyl is on the opposite side of the benzene ring over the rigid solid bond. The predominant application for cinnamaldehyde is in the flavor and fragrance industries. It is used as a flavouring for chewing gum, ice cream, candy, and beverages. is used in some perfumes of natural, sweet, or fruity scents. A variety of alkyl substituted cinnamaldehyde derivatives including amyl and hexyl cinnamicaldehydes are also widely used in flavouring additives. They imparts a cinnamon odor to soaps and household products. Cinnamaldehyde is also used as a fungicide or insecticide. Cinnamaldehyde is also used as a corrosion inhibitor in combination with additional components such as dispersing agents, solvents and other surfactants for steel and other ferrous alloys in corrosive fluids.
DESCRIPTION OF ALDEHYDE: Aldehydes are organic compounds containing -CHO radical, in which a carbon atom forms a solid bond with an oxygen atom and is also bonded to a hydrogen atom and another group denoted by R, which can be a second hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, or an aryl group. The most important and the simplest examples are methanal (formaldehyde), HCOH, and ethanal (acetaldehyde), CH3CHO.( In systematic chemical nomenclature, aldehyde names end with the suffix -al). Formaldehyde is used to make synthetic resins by reaction with phenols, urea, and melamine, as a chemical intermediate, as an embalming fluid, and as a disinfectant. Acetaldehyde is used chiefly to manufacture acetic acid. They are unpleasant-smelling liquids widely used in the chemical industry, whereas aromatic aldehydes frequently have pleasant smells and are used widely as flavourings and perfumes. An example is benzaldehyde (benzenecarbaldehyde, C6H5CHO), a derivative of benzene with an aldehyde group attached to the ring. It is a colourless oil smelling of almonds offer applications to both in perfumes and flavourings. Aldehydes are formed by oxidation of primary alcohols; further oxidation yields carboxylic acids. Aldehydes have certain characteristic addition and condensation reactions. Aldehydes can be reduced to primary alcohols (ketones to secondary alcohols). Aldehydes form cyanohydrins with hydrogen cyanide, acetals with alcohol, yellow-orange solid derivatives with DNP ( 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazones) and undergo condensation reactions to yield oximes (compounds containing the group C:NOH), hydrazones (organic compounds containing the group =C:NNH2), and semicarbazones (organic compounds containing the unsaturated group =C:N.NH.CO.NH2). Aldehydes readily polymerize.
APPEARANCE
REFRACTIVE INDEX
HAZARD OVERVIEW
Combustible Liquid, Skin sensitiser, Corrosive
GHS
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H315-H317-H319-H335
P STATEMENTS
P261-P280-P305 + P351 + P338
![]()
RISK PHRASES
36/37/38-43
SAFETY PHRASES
26-36/37
PRICE INFORMATION