PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
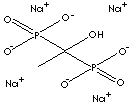
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
clear to yellow liquid
miscible
REFRACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
clear to yellow viscous liquid
ACTIVE ACID
25.0% min
ACTIVE SALT
35.0% min
CHLORIDE
1.0% max
IRON
35ppm max
PHARMACEUTICAL APPLICATION OF BIPHOSPHONATE
Biphosphonate, a salt, ester, or anion of a dimer of phosphonic acid (diphosphonic acid), inhibits bone resorption as a sodium salt and complexed with technetium Tc 99m for bone imaging. The monophosphonates are not active. Biphosphonates are used in disorders affecting the skeleton such as osteoporosis, metastatic disease, and Paget's disease. While bisphosphonates are analogues of endogenous pyrophosphate structurally, they are characterized by a P-C-P bond, the linking oxygen is replaced with a carbon, which is resistant to enzymatic and chemical hydrolysis. General structure is
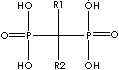
Side chains are
responsible for chemical-physicla properties, mechanism of resorption, and
pharmacokinetics. It is known that biphosphonates bind strongly to
hydroxyapatite crystals at the sites of increased bone turnover preferentially
and inhibit the formation, aggregation, and dissolution of the crystals.They
also may inhibit osteoclast function directly, promotion of osteoclast
apoptosis, and interference with osteoblast-mediated osteoclast
activation.
Bisphosphonate products include: (see belows)
- Etidronic acid (CAS #: 2809-21-4)
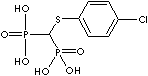
- Clodronic acid (CAS #: 10596-23-3)
- Tiludronic acid (CAS #: 89987-06-4)
- Medronic acid (CAS #: 1984-15-2)
- Pamidronic acid (CAS #: 40391-99-9)
- Neridronic acid (CAS #: 79778-41-9)
- Olpadronic acid (CAS #: 63132-39-8)
- Alendronic acid (CAS #: 66376-36-1)
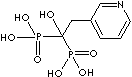
- Ibandronic acid (CAS #: 114084-78-5)
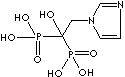
- Risedronic acid (CAS #: 105462-24-6)
- Zoledronic Acid (CAS #: 118072-93-8)
|
Biphosphonate |
CAS # |
Side
Chains |
STRUCTURE |
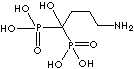
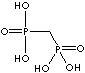
| Alendronic acid (Alendronate) |
66376-36-1 |
R1=
-OH |
|
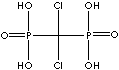
| Clodronic acid (Clodronate) |
10596-23-3 |
R1=
-Cl |
|
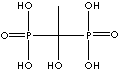
| Etidronic acid (Etidronate) |
2809-21-4 |
R1=
-OH |
|
| Ibandronic acid (Ibandronate) |
114084-78-5 |
R1=
-OH |
|
| Medronic acid (Medronate) |
1984-15-2 |
R1=
-H |
|
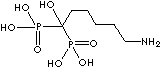
| Neridronic acid (Neridronate) |
79778-41-9 |
R1=
-OH |
|
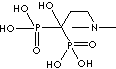
| Olpadronic acid (Olpadronate) |
63132-39-8 |
R1=
-OH |
|
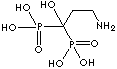
| Pamidronic acid (Pamidronate) |
40391-99-9 |
R1=
-OH |
|
| Risedronic acid (Risedronate) |
105462-24-6 |
R1=
-OH |
|
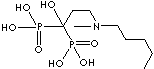
| Tiludronic acid (Tiludronate) |
89987-06-4 |
R1=
-H |
|
| Zoledronic Acid (Zoldronate) |
118072-93-8 |
R1=
-OH |
|
PRICE INFORMATION