PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
MELTING POINT
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
Sparingly soluble
REFRACTIVE INDEX
1.478 - 1.483
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS
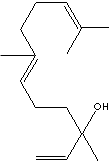
Nerolidol is present in neroli, ginger, jasmine, lavender, tea tree and lemon grass. The aroma of nerolidol is woody and reminiscent of fresh bark. It is used as a flavoring agent and in perfumery. It was also shown to be produced by the leaves of a large number of plant species in response to herbivory insects and then to be transformed into a C11-homoterpene (4,8-dimethyl-1,3,7-nonatriene) which attracts predatory insects (Dicke M et al., J Chem Ecol 1990, 16: 3091–3118). (http://www.cyberlipid.org/)
Geraniol is a monoterpenoid C-10 (branched) alcohol found widely as a chief constituent in essential oils including ilang-ilang oil, palmarosa oil, geranium oil, orange flower oil, lemongrass oil, hops oil, and lavender oil. It is a clear to pale-yellow liquid; boiling point 230 C; insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol, ether and most common organic solvents. It is the major constituent of rose-like odor. It is used in perfumery and flavoring. Nerol is the cis-isomer of geraniol. Geranial and neral are the corresponding aldehydes. Citronellol is the dihydrogeraniol and citronellal is the corresponding aldehyde. Citral is the mixture of geranial (trans-citral, called citral A) and neral (cis--citral, called citral A). Citral is the major constituent of emongrass oil, verbena oil, lemon oil, nikkel oil, lime oil, ginger oil, and other plant essential oils. It is the main source of lemon odor. Neral has a less intense, but sweeter. Citral is also used as a flavor. Citral is used as a raw material in the synthesis ionone which is a perfumery and flavoring component itself and used in the production of retinol. Geraniol is a pheromone of certain species of bees, being secreted by the scent glands of worker bees to signal the location of nectar-bearing flowers and the entrances to their hives. Geraniol also find an application as an insect repellants or deterrants.
Nerolidol is one of ingredient in fragrance. It's end applications include soap, detergent, beauty care product, household product. (Olfactive Note : fruit, floral, soapy, woody )
APPEARANCE
FEMA No.:2772
GERANIOL MOLECULES