PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
229-146-5
CLASSIFICATION
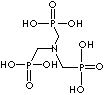
Phosphonic Acid, Chelating agent, Water treatment
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
white solid
miscible
REFRACTIVE INDEX
1.427
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
PubChem Compound Summary - Nitrilotris(methylene)triphosphonic acid
http://www.inchem.org/
The
product as manufactured (50% solution) is used exclusively for industrial
applications or for formulation. Used as an anti-scaling agent in
industrial water cooling. Used as an anti-scaling agent in industrial
boilers Used as an anti-scaling or bleach stabilisation agent in
formulation into cleaners (industrial and institutional: I &
I). In I & I cleaners the concentration is typically at the
0.2-0.5% range. The product is used typically at the 1-5mg/l range.
For the first two uses the product is either used as such or reformulated
by specialist water treatment companies for specific application
purposes.
Local:
Phosphonates derived from phosphorous (phosphonic) acid are employed in the
applications of scale Inhibition, sequestration, dispersion and corrosion
inhibition in addition to the main applications of agricultural chemicals such
as fertilizers, pesticides, and soil conditioners. Phosphonates offer a wide
range of sequestrants to control metal ions in aqueous systems. By forming
stable water soluble complexes with multivalent metal ions, phosphonates prevent
undesired interaction by blocking normal reactivity of metal ions. This ability
contributes to function as threshold industrial water treatment and metal
treatment processes (antiscalants, corrosion inhibitors, chelants, sludge
conditioners, pulp bleachings, deflocculants, dispersants, metal cleaners,
electroplating and crystal growth modifiers). Phosphonates are also used in
manufacturing detergents, cosmetics and personal care products for special
functions such as low levels iron control, stain removal, bleach stabilization,
peroxide stabilization and anti-encrustation. Phosphonates existing in various
compounds as acids or salts are marketed in the form of concentrated solutions.
List of Aminotrimethylene phosphonic acid salts
- Aminotrimethylene phosphonic acid pentasodium salt (CAS RN: 2235-43-0)
- Aminotrimethylene phosphonic acid hydrochloride (CAS RN: 20592-85-2)
- Aminotrimethylene phosphonic acid potassium salt (CAS RN: 27794-93-0)
- Aminotrimethylene phosphonic acid ammonium salt (CAS RN: 34274-28-7)
- Aminotrimethylene phosphonic acid hexapotassium salt (CAS RN: 40588-62-3)
- Aminotrimethylene phosphonic acid zinc salt (CAS RN: 68413-74-1)
- Aminotrimethylene phosphonic acid triammonium salt (CAS RN: 72333-13-2)
- Aminotrimethylene phosphonic acid pentapotassium salt (CAS RN: 94021-26-8)
- Aminotrimethylene phosphonic acid tetraammonium salt (CAS RN: 94021-27-9)
- Aminotrimethylene phosphonic acid hexaammonium salt (CAS RN: 94021-28-0)
APPEARANCE
clear liquid
50.0% min
CHLORIDE
1.0% max
IRON
30ppm max
COLOR, APHA
150 max
1760
HAZARD OVERVIEW
Corrosive. May cause central nervous system effects. May cause cardiac disturbances. Causes eye and skin burns. May cause severe respiratory tract irritation with possible burns. May cause severe digestive tract irritation with possible burns. Target Organs: Central nervous system, cardiovascular system.
GHS
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H314 Causes severe skin burns and eye damage
H318 Causes
serious eye damage
PRECAUTIONARY STATEMENTS
P301 + P330 + P331 IF SWALLOWED: rinse mouth. Do NOT induce
vomiting
P280 Wear eye protection/face protection
P305
+ P351 + P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for
several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do.
Continue rinsing
P310 Immediately call a POISON CENTER
or doctor/physician
![]() C
Corrosive
C
Corrosive
RISK PHRASES
34 Causes burns.
SAFETY PHRASES
26 In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with
plenty of water and seek medical advice.
36/37/39 Wear
suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection.
45
In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice
immediately (show the label where possible).