| CAS
NO. |
7541-49-3 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
310-127-6 |
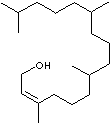
| FORMULA |
C20H40O |
| MOL
WT. |
296.54
|
|
H.S.
CODE
|
2905.22 |
| TOXICITY
|
|
|
SYNONYMS |
mixture
of cis-, trans-Phytol; |
|
3,7,11,15-Tetramethyl-2-hexadecen-1-ol;
3,7,11,15-Tetramethyl-2-hexadecen-1-ol,
mixed isomers; |
|
SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
clear
to slightly yellow liquid |
|
MELTING
POINT
|
|
| BOILING
POINT |
202
- 205 C at 15 hPa |
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
0.845
- 0.855 |
|
SOLUBILITY
IN WATER
|
Insoluble |
| pH |
|
| VAPOR
DENSITY |
|
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
1.4620
- 1.4680 |
| NFPA
RATINGS |
Health:
1; Flammability: 1; Instability:
0 |
| FLASH
POINT |
187
C |
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
| Phytol,
an acyclic terpenoid, is
used in manufacturing synthetic vitamins E and K. It
is an ingredient of fragrances.
It's end applications include soap, detergent,
beauty care product, household product.
(Olfactive Note : fruit,
balsamic.) |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
clear
to slightly yellow liquid |
| PURITY |
95.0%
min (cis + trans) |
| trans |
60.0%
min
|
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
0.845
- 0.855 |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
185kgs
in drum |
| HAZARD
CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
| European
Hazard Symbols: N, Risk Phrases:
36/38,
Safety
Phrases: 26-36 |
| GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF TERPENE
|
A class of
naturally occurring compounds mainly in plants as constituents of essential oils
whose carbon skeletons are composed exclusively of isoprene C5 units
(CH2=C(CH3)-CH=CH2). Most terpenes are
hydrocarbons having molecular formula (C5H8)n in a cyclic or
acyclic, saturated or unsaturated structure, while the terpenoids are
oxygen-containing analogues of the terpenes such as alcohols, aldehydes or
ketones containing hydroxyl groups or carbonyl groups. Several vitamines,
hormones, flavour and flagrances and latex are terpenoids. Terpenes containing
30 or more carbons are usually formed by the fusion of two terpene precursors in
a regular pattern, usually head-to-tail appears to be violated. They are differ
from one another not only in functional groups but also in their basic carbon
skeletons. Terpenes are employed mainly the fragrance and flavour purpose, as
well as in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries. They are classified by
the number of isoprene units:
|
Class |
number of
isoprene |
Examples |
|
Hemiterpene |
1
(C5H8) |
Found in associated with Alkaloids, Coumarins
and Flavonoids. |
|
Monoterpenes |
2
(C10H16) |
Geraniol, Citronellol, Pinene, Nerol, Citral,
Camphor, Menthol, Limonene, Thujone |
|
Sesquiterpenes |
3
(C15H24) |
Nerolidol, Farnesol |
|
Diterpenes |
4
(C20H32) |
Phytol, Vitamin A1 |
|
Triterpenes |
6
(C30H48) |
Squalene |
|
Tetraterpenes |
8
(C40H84) |
Carotene (Provitamin A1) |
|
Polyterpenes |
>10 (C5H8)n |
|
|
