| CAS
NO. |
127-91-3,
18172-67-3 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
242-060-2 |
| FORMULA |
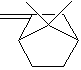
C10H16 |
| MOL
WT. |
136.24 |
| H.S.
CODE |
2902.19 |
| TOXICITY |
|
| SYNONYMS |
6,6-Dimethyl-2-methylenebicyclo[3.1.1]heptane;
|
|
(1S,5S)-(-)-2(10)-Pinene; (-)-beta-Pinene;
(-)-2(10)-Pinene; L-beta-pinene; (1S)-(-)-beta-Pinene; laevo-beta-Pinene; (1S)-6,6-Dimethyl-2-methylene
bicyclo [3.1.1]heptane; |
| PRICE |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
Clear
liquid |
| MELTING POINT |
-61 C
|
| BOILING
POINT |
164 -165
C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
0.86 - 0.869 |
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
Insoluble |
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
255 C |
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
Health: 1 Flammability: 2 Reactivity: 0 |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
1.4775 - 1.4785 |
| FLASH
POINT |
36
C
|
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary conditions |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS
|
|
Turpentine is a
semifluid substance consisting of two principal components, spirits of
turpentine (volatile portion also known as oil of turpentine or turps ) and a
type of rosin (nonvolatile portion also known as colophony). Turpentine is
exuded from coniferous trees. The crude turpentine is distilled through steam
into commercial turpentine, oil of turpentine. The pure turpentine oil is a
transparent oily liquid with a penetrating odor and a characteristic taste.
Turpentine is not a pure substance but a complex mixture of terpenes,
particularly large proportion of pinene (bicyclic monoterpenic hydrocarbon), a
compound from which camphor is manufactured. Terpene is a class of naturally
occurring unsaturated hydrocarbons whose carbon skeletons are composed
exclusively of isoprene C5 units (CH2=C(CH3)-CH=CH2), consisting of five carbon atoms attached to eight
hydrogen atoms (C5H8). The stepwise
distillation with water and carbonates yields terpenes. The most abundant monoterpene
is pinene.
There are two isomerers called alpha (or
beta) pinene. The alpha form boils at 156-160 C, and of the beta form boils at
164-169C. It is used as solvents for paints, coatings and wax formulations. It
is used as an intermediate for resins and for camphor, menthol, campholenic aldehyde
and terpineol.
It is used as lube-oil additives. Myrcene,one
of the most important chemicals used in the perfumery industry,
is
obtained from beta-Pinene
through
pyrolysis.
|
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
clear
liquid |
| alpha-PINENE |
95.0%
min |
|
COLOR,
APHA
|
50
max
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
170kgs
in drum |
| HAZARD CLASS |
3
(Packing Group: III) |
| UN
NO. |
2319 |
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
Hazard
Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 10-20/21/22-36/38-43-51/53-65, Safety Phrases: 36/37-46-61-62 |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF TERPENE
|
A class of naturally occurring compounds mainly in plants as constituents of
essential oils whose carbon skeletons are composed exclusively of isoprene C5
units (CH2=C(CH3)-CH=CH2). Most terpenes are hydrocarbons having molecular
formula (C5H8)n in a cyclic or
acyclic, saturated or unsaturated structure,
while the terpenoids are oxygen-containing analogues of the terpenes such as
alcohols, aldehydes or ketones containing hydroxyl groups or carbonyl groups.
Several vitamines, hormones, flavour and flagrances and latex are terpenoids.
Terpenes containing 30 or more carbons are usually formed by the fusion of two
terpene precursors in a regular pattern, usually head-to-tail appears to be
violated. They are differ from one another not only in functional groups but
also in their basic carbon skeletons. Terpenes are employed mainly the fragrance
and flavour purpose, as well as in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries.
They are classified by the number of isoprene units:
|
Class
|
number of isoprene
|
Examples
|
|
Hemiterpene
|
1
(C5H8)
|
Found in associated with
Alkaloids, Coumarins and Flavonoids. |
|
Monoterpenes
|
2
(C10H16)
|
Geraniol, Citronellol, Pinene, Nerol, Citral, Camphor, Menthol, Limonene,
Thujone |
|
Sesquiterpenes
|
3
(C15H24)
|
Nerolidol, Farnesol |
|
Diterpenes
|
4
(C20H32)
|
Phytol, Vitamin A1 |
|
Triterpenes
|
6
(C30H48)
|
Squalene |
|
Tetraterpenes
|
8
(C40H84)
|
Carotene (Provitamin A1) |
|
Polyterpenes
|
>10
(C5H8)n |
|
|
