PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
MELTING POINT
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
REFRACTIVE INDEX
186 C
Sulfur combines with nearly all elements. Sulfur forms ring and chain structures as it is the second only to carbon in exhibiting catenation. The 8-membered ring and shorter chain structure of sulfur molecule is important in vulcanization process which individual polymers are linked to other polymer molecules by atomic bridges. This process produces thermoset materials which are cross-linked and irreversible substances. The term thermoplastic is for high molecular weight polymers which can undergo melting-freezing cycle. Thermosets are not melted and re-molded on heating after cured. The split of sulfur 8-membered ring structure into shorter chains provides rubber vulcanization process. The split are liked with cure sites (some of the solid bonds in the molecule) on rubber molecules, resulting in forming sulfur bridges typically between 2 and 10 atoms long. Vulcanization makes rubber harder, more durable and more resistant to heating, aging and chemical attacks. The number of sulfur atoms in the sulfur bridges varies physical properties of the end products. Short bridges containing one or two sulfur atoms offer heat resistance and long bridges offer flexible property. Vulcanization can also be accomplished with certain peroxides, gamma radiation, and several other organic compounds. The principal classes of peroxide cross-linking agents are dialkyl and diaralkyl peroxides, peroxyketals and peroxyesters. Other vulcanizing agents include amine compounds for the cross-linking of fluorocarbon rubbers, metal oxides for chlorine-containing rubbers (notably zinc oxide for chloroprene rubber) and phenol-formaldehyde resins for the production of heat-resistant butyl rubber vulcanizates. Accelerator, in the rubber industry, is added with a curing agent to speed the vulcanization. Accelerators contain sulfur and nitrogen like derivatives of benzothiazole and thiocarbanilides. The popular accelerators are sulfenamides (as a delayed-action accelerators), thiazoles, thiuram sulfides, dithocarbamates and guanidines.
There are some types of rubber accelerators. They are used in combination with each other in accordance with vulcanizing and/or acid-base conditions. Some examples classified by chemical structure are as below;
- Thiazole
- 2-Mercaptobenzothiazole (CAS #: 149-30-4)
- Dibenzothiazole disulfide (CAS #: 120-78-5)
- 2-Mercaptobenzothiazole Zinc salt (CAS #: 155-04-4)
- Sulphenamide
- N-Cyclohexyl-2-benzothiazole sulfenamide (CAS #: 95-33-0)
- N-Oxydienthylene-2-benzothiazole sulfenamide (CAS #: 102-77-2)
- N-tert-butyl-2-benzothiazyl sulfenamide (CAS #: 95-31-8)
- Guanidine
- Diphenyl guanidine (CAS #: 102-06-7)
- Di-o-tolylguanidine (CAS #: 97-39-2)
- Thiuram
- Tetramethyl thiuram disulfide (CAS #: 137-26-8)
- Tetraethyl thiuram disulfide (CAS #: 97-77-8)
- Tetramethyl thiuram monosulfide (CAS #: 97-74-5)
- Isobutyl thiuram disulfide (CAS #: 3064-73-1)
- Tetrabenzylthiuram disulfide (CAS #: 10591-85-2)
- Dipentamethylene thiuramtetrasulfide (CAS #: 120-54-7)
- Dithiocarbamate
- Zinc dimethyl dithiocarbamate (CAS #: 137-30-4)
- Zinc diethyl dithiocarbamate (CAS #: 14324-55-1)
- Zinc dibutyl dithiocarbamate (CAS #: 136-23-2)
- Zinc N-ethyl-dithiocarbamate (CAS #: 14634-93-6)
- Zinc dibenzyl dithiocarbamate (CAS #: 14726-36-4)
- Copper dimethyl dithiocarbamate (CAS #: 137-29-1)
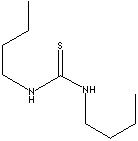
- Thiourea
- Ethylene thiourea (CAS #: 96-45-7)
- N,N'-Diethylthiourea (CAS #: 105-55-5)
- N-N'-Diphenylthiourea (CAS #: 102-08-9)
APPEARANCE
97.0% min
PRICE