PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
110-62-3
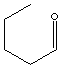
203-784-4
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
MELTING POINT
0.808 - 0.818
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
1.3925 - 1,3945
APPLICATIONS
Aldehydes are organic compounds containing -CHO radical, in which a carbon atom forms a solid bond with an oxygen atom and is also bonded to a hydrogen atom and another group denoted by R, which can be a second hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, or an aryl group. The most important and the simplest examples are methanal (formaldehyde), HCOH, and ethanal (acetaldehyde), CH3CHO.( In systematic chemical nomenclature, aldehyde names end with the suffix -al). Formaldehyde is used to make synthetic resins by reaction with phenols, urea, and melamine, as a chemical intermediate, as an embalming fluid, and as a disinfectant. Acetaldehyde is used chiefly to manufacture acetic acid. They are unpleasant-smelling liquids widely used in the chemical industry, whereas aromatic aldehydes frequently have pleasant smells and are used widely as flavourings and perfumes. An example is benzaldehyde (benzenecarbaldehyde, C6H5CHO), a derivative of benzene with an aldehyde group attached to the ring. It is a colourless oil smelling of almonds offer applications to both in perfumes and flavourings. Aldehydes are formed by oxidation of primary alcohols; further oxidation yields carboxylic acids. Aldehydes have certain characteristic addition and condensation reactions. Aldehydes can be reduced to primary alcohols (ketones to secondary alcohols). Aldehydes form cyanohydrins with hydrogen cyanide, acetals with alcohol, yellow-orange solid derivatives with DNP ( 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazones) and undergo condensation reactions to yield oximes (compounds containing the group C:NOH), hydrazones (organic compounds containing the group =C:NNH2), and semicarbazones (organic compounds containing the unsaturated group =C:N.NH.CO.NH2). Aldehydes readily polymerize. n-Valeraldehyde, straight C5 chain aldehyde, is used as an intermediate in the manufacture of alcohols, acids, esters, amines and other organic compounds.
APPEARANCE
WATER
0.15% max
ACID VALUE
2.0 max (mg KOH/g)
15 max