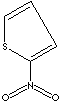
The prefix
nitro- indicates the presence of NO2- radical, while
nitrate refers to any salt or ester of nitric acid or the
NO3- anion. Nitroso- is
the prefix indicating presence of the group -NO and azo- is for -N=N- group.
Some range of organic compounds containing nitrogen include nitro compounds
(RNO2 ), nitroso compounds
(RNO), amines (R3N ), amino acids, and
natural alkaloids or nucleotides. The nitrogen ion in nitro compounds is
trigonally planar with 120° angles. There are two resonance bonds so that the
two oxygens are equivalent. Nitro compounds are strongly basic due to electron
withdrawing both inductively and mesomerically. Historically, they are
abundant in dyes and explosives. Nitro compounds,
organic hydrocarbons having one or more NO2 groups bonded via
nitrogen to the carbon framework, are versatile intermediate in organic
synthesis.
- Michael
addition
- Reduction
- Henry
Reaction (Nitro-aldol reaction)
- Nef
reaction
- O-Alkylation
- Cycloaddition
- Substitution, Elimination, Conversion
reaction
- Alkylation,
Acylation, and Halogenation
Thiophene, also known as thiofuran, is a cyclic compound containing four carbon
atoms and one sulfur atom in the ring. Thiophene is an analog to furan and pyrrole where the sulfur
atom is replaced by O and NH
respectively. Thiophene is a toxic, flammable, and colorless liquid; insoluble in water (soluble in most
organic solvents including alcohol and
ether); melting at -38 C, boiling at 84 C. Thiophene is the simplest aromatic
compound containing sulfur atom and it shares some similar
chemical properties with benzene. The lone electron pairs on sulfur in the delocalized pi electron system does
not exhibits the properties of thioethers but aromaticity.
The sulfur atom is unreactive but the adjacent carbons
are susceptible to attack
by electrophiles. It is reactive toward sulfonation. In commercial thiophene
can be prepared by the reaction of butane and sulfur.
Thiophenes are also prepared by the reaction of diketones with Lawesson's
reagent. Thiophene and its derivatives exist in petroleum or coal. Thiophene derivatives
are also found in natural plant pigments. Biotin, a water-soluble B-complex vitamin,
is a reduced thiophene derivative. Thiophene moiety
is found in ccphalothin antiboitics. Thiophene is used as a solvent and chemical intermediate. Its
derivatives are used in manufacturing dyes, aroma compounds and
pharmaceuticals. They are used as monomers to make
condensation copolymers. Organic conductive polymers are responsible for the
important materials science for the application of polymer
electro
luminescence. |