PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
FLASH POINT
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Glutamine is a conditionally essential amino acid that is needed more from supplementation than the amount from body's synthesis under serious physical stress. Glutamine is an important for carrying urinary ammonia and for the removing of waste ammonia in the body and for the normal brain function and digestion. Glutamine plays an important role in the immune system for energy. The deficiency can slow the healing process and the immune system would be impaired. Glutamine is not good for parenteral solution due to instability. Acetyl-, glycyl-, or alanylglutamine are for parenteral uses.
Glutamine (Gln) is the most abundant free amino acid in the body and plays a vital role in amino acid transport and nitrogen balance. Gln is also a primary fuel for rapidly dividing cells such as enterocytes and lymphocytes, which protect mucosa barricade and enhance immune functions[1]. Patients undergoing elective abdominal surgery usually have malnutrition and Gln concentration is low in blood due to several factors: mechanical obstruction, limitation of food intake, tumor-induced cachexia, obstruction of pancreaticobiliary, malabsorption and ongoing blood loss. Moreover, intravascular and free muscle glutamine pools become depleted in response to perioperative abrosia and operative stress. Free Gln is lack of stability in solution and intravenous adminitration is limited. Glutamine dipeptide (L-alanyl-L-glutamine) can be taken via vein and hydrolyzed into glutamine in circulation as Gln substitution. It was given to patients undergoing abdominal surgery in order to improve their postoperative nitrogen balance and immunonutrition[2]. Therefore, it is worth knowing whether routine supplementation of glutamine dipeptide in parenteral nutrition (PN) can amend clinical outcomes. Meta-analysis has been applied in medical research to improve statistical effi ciency, to evaluate the disadvantage of established studies and to draw reliable conclusions from various potentially relevant studies. It is the most promising approach for future research and a guideline for clinical treatment[3]. This meta-analysis aims to enhance our understanding of the clinical and economical validity of glutamine dipeptide for patients undergoing abdominal surgery. (http://www.wjgnet.com/)
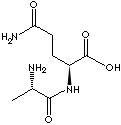
Alanylglutamine is a dipeptide composed of two amino acids L-Alanyl and L-glutamine. It is a white to off-white crystalline powder with faintly sweet taste. It is soluble in water; undissolved in ethanol, acetone and ether.
APPEARANCE
PURITY
99.0% min
1.0% max
10ppm max