PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
Health: 3, Flammability: 0, Reactivity: 1
AUTOIGNITION
FLASH POINT
APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
97.0% min
Amidines ( -HN=CNH2) and guanidines [-HN=C(NH2)2] are strongly basic reagents. Bases activation of deprotonation is the first step in the synthesis. The strength of basicity, nucleophilicity, steric hindrance or solubility are the factors to select reagents for the best results in the chemical reactions such as alkylation, tautomerization, dehydrohalogenation, michael-addition, esterification, saponification, acylation, silylations, aldol-condensation, eliminations, and cyclization. The order of basicity strength of some amines are; TBD > MTBD > DBU > DBN > TMG > Quinuclidine > TMP, Pempidine > Triethylamine > TED > Tributylamine > Collidine > Lutidine
- TBD: 1,5,7-Triazabicyclo(4.4.0)dec-5-ene; 1,3,4,6,7,8-Hexahydro-2H-pyrimido[1,2-a] pyrimidine, CAS #: 5807-14-7
- MTBD :7-Methyl-1,5,7-triazabicyclo(4.4.0)dec-5-ene;1,3,4,6,7,8-Hexahydro-1- methyl-2H-pyrimido [1,2-a]pyrimidine, CAS #: 84030-20-6
- DBU: 1,8-Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene; 2,3,4,6,7,8,9,10-Octahydropyrimidol[1,2-a] azepine, CAS #: 6674-22-2
- DBN: 1,5-Diazabicyclo[4.3.0]non-5-ene, CAS #: 3001-72-7
- TMG: 1,1,3,3-Tetramethylguanidine; N,N,N',N'-Tetramethylguanidine, CAS #: 80-70-6
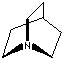
- Quinuclidine: 1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]octane, CAS #: 100-76-5
- TMP: 2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine, CAS #: 768-66-1
- Pempidine: 1,2,2,6,6-Pentamethylpiperidine, CAS #: 79-55-0
- TED: 1,4-Diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octan; Triethylenediamine, CAS #: 280-57-9
- Collidine: Trimethylpyridine, CAS #: 108-75-8 (2,4,6- Isomer)
- Lutidine: Dimethylpyridine, CAS #: 108-48-5 (2,6- Isomer)