PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
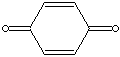
108.1
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
Oral rat LD50: 100mg/kg
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
yellow to green crystalline solid with pungent odor
116 C
1.32
3.7
REFRACTIVE INDEX
435 C
74 C
Stable under ordinary conditions
APPLICATIONS
Quinone is a group of aromatic compounds containing two opposite carbonyl groups (C=O) and the other two pairs of carbon atoms linked by vinylene group(-CH=CH) in a six-membered unsaturated ring. The carbonyl groups are located in different rings and form various chemical structures which offer important roles to colours. Quinones are used in photography and dye manufacture. Quinones occur benzoquinones, naphthoquinones, anthraquinones, and polycyclic quinones. Though quinones are found in plants and in a few animals, they usually are prepared by oxidation of aromatic amines, polyhydric phenols, and polynuclear hydrocarbons.The reduction of quinone to the corresponding dihydroxy form is an important characteristic reaction. In acidic solution, p-benzoquinone is reduced reversibly to hydroquinone. The so-called quinhydrone electrode, containing equimolar solution of quinone and hydroquinone, is used to determine hydrogen ion concentrations depends on the oxidation-reduction reactions. Hydroquinone and its derivatives used principally in photographic dye chemicals, in medicine, as an antioxidant, and in paints, varnishes, and motor fuels and oils. Hydroquinone and certain derivatives are also used as polymerization inhibitors by direct reacting with peroxy-free radical to tie up free radicals. p-Benzoquinone is used as a fungicide and to make dyes and other agrochemicals. It is also an inhibitor especially for vinyl monomers and unsaturated polyester resins, and cross-linking agent.
Examples of quinone substances
|
Quinone substances |
Description |
| Ansamycin antibiotics | Chemotherapeutic |
|
Anthracycline |
Chemotherapy |
|
Anthraquinone |
Polycyclic aromatic compound |
| Alizarin | Anthraquinone dye |
|
Quinones |
Oxidants in organic synthesis |
|
Blattellaquinone |
Pheromone |
| Chloranil | Oxidant, Pesticide |
|
Coenzyme Q10 |
Vitamin-like substance |
| Emodin | Enzyme inhibitors |
| Carminic acid | Anthraquinone dye |
|
Indolequinones |
Indoles |
|
Lapachol |
Vitamin K-like substance |
|
Lawsone |
Dye |
|
Menadione |
Vitamin K1 |
|
Mitomycin |
Chemotherapeutic |
|
Naphthoquinones |
Aromatic ketone |
|
Pixantrone |
Immunosuppressant |
|
Plastoquinone |
Photosynthesis |
|
Pyrroloquinoline quinone |
Enzyme cofactor |
| Tanespimycin | Antineoplastic |
|
Vitamin K |
Vitamin |
APPEARANCE
yellow to green crystalline solid
ASSAY
99.5% min
ASH
0.2% max
WATER
0.1% max
- Aldol Reactions
- Alkylation of Enolate Anions
- Clemmensen Reduction
- Cyanohydrin Formation
- Enamine Formation
- Hemiacetal and Acetal Formation
- Hydration Formation
- Imine Formation
- Wolff-Kishner Reduction
OTHER INFORMATION