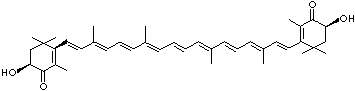
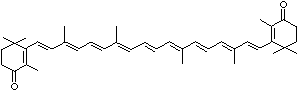
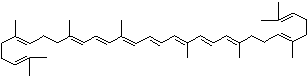
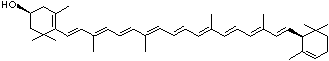
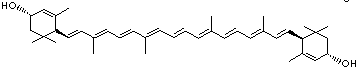
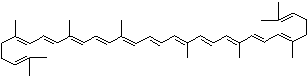
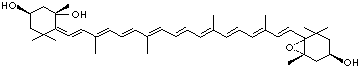
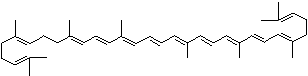
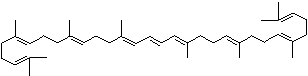
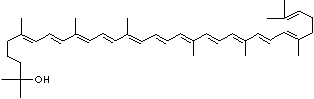
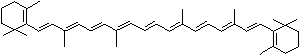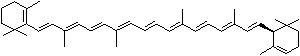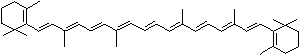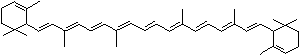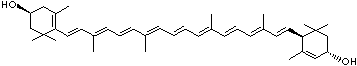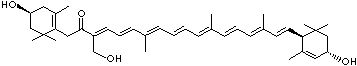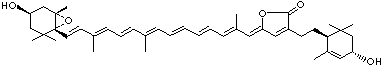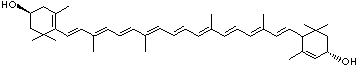| beta-CAROTENE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO. | 7235-40-7 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 230-636-6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FORMULA | C40H56 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 536.90 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
H.S. CODE |
2936.10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS |
Trans-Beta-Carotene; Provatene; Provitamin A; Natural Yellow 26; |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| á,á-caroteno (Spanish); beta,beta-carotene; 1,1'-(3,7,12,16-tetramethyl-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17- Octadecanonaene-1,18-diyl) Bis(2,6,6-trimethyl-, (All-e)-Cyclohexene; | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
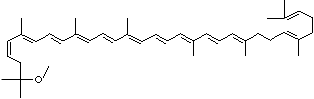
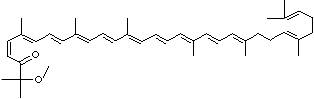
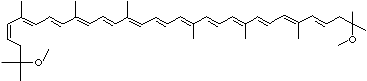
| SMILES |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CLASSIFICATION |
NATURAL COLORANT / VITAMINS / CAROTENOIDS / |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE | red to brown powder or crystals | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT | 176 - 183 C (Decomposes) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | insoluble | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pH | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPLICATIONS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carotenoids are plant pigments that involve in light harvesting to
participate in energy transfer process in photosynthesis. They absorb light in
the 400-500 nm region of the visible spectrum and impart coloration of yellow,
orange, red, and purple. They are widely distributed in nature including
vegetables, fruits, insects, fishes, and birds. Animals are incapable of
synthesizing carotenoids, which should be obtained through diet. Chlorophyll is
the generic name for green plant pigments which includes the open-chain bile
pigments and the large ring compounds. The structure of chlorophyll molecule has
four nitrogen-containing pyrrole rings bonded to a central magnesium atom, and
the fifth ring containing only carbon atoms, and various long hydrocarbon tails
attached to the pyrrole rings. Carotenoids contain sequences of conjugated
isoprene units, alternating double and single carbon bonds. They are sometimes
terminated by cyclic end-groups (rings) complemented with hydroxylated, oxidized
and hydrogenated groups. The conjugated double bonds absorbs light and UV. The
more number of double bonds result in the absorbance of red color wavelength.
Changes in geometrical configuration about the double bonds result in the
existence of many cis- and trans- isomers. Carotenoids are usually located in
quantity in the grana of chloroplasts in the form of carotenoprotein complexes
which give blue, green, purple, red, or other colors to the outer surfaces in
plants, or eggs of crustaceans, such as the lobster and crab. Carotenoids are
classified into carotenes (un-oxidized carotenoids, orange pigments) or xanthophylls
(yellow pigments) which
contains oxygen and are alcohol-soluble. It is known that more than 600
carotenoids are isolated from natural sources.
Carotene: though carotene is the simplest of a group of natural pigments called carotenoids, it has an unsaturated and long aliphatic hydrocarbon chain. It is found as a fat-soluble pigment in many higher plants of dark green leafy and yellow vegetables such as carrots, collards, turnips, sweet potatoes, and squash, and in yellow fruits such as apricots, oranges, peaches, and cantaloupes. Carotene is thought to transport light energy for photosynthesis or contribute to reduction reaction. It is important in animal biology as it is are converted to retinol in the body by an enzyme in the intestinal wall and the liver. Carotene occurs in several isomeric forms: alpha, beta, gamma, delta, epsilon, and zeta of which the form of beta acts as an antioxidant nutrient protecting the body from damaging molecules called free radicals and an immune system booster as it is converted to vitamin A (retinol), important in animal biology as the main dietary source. One molecule of beta-carotene splits into two molecules of vitamin A and thus Beta-carotene is called provitamin A. Cryptoxanthin is a yellow carotenoid widely distributed in egg yolk, green grass, yellow corn which can be converted into vitamin A in the body. Cryptoxanthin is the major precursor of vitamin A together with beta-carotene in humans. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CRYSTALLINE
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
Dark red power or crystal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CONTENT |
98% min |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HEAVY METALS | 20ppm max | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ARSENIC |
3ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LOSS ON DRYING |
1.0% max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
RESIDUE ON IGNITION |
0.1% max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLUID SUSPENSION 30% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
red viscous oil | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CONTENT |
30.0% min | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HEAVY METALS | 20ppm max | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ARSENIC |
3ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING |
250mg/can
(98%), 1kg/can (30%)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EXAMPLES OF NATURALLY-OCCURRING CAROTENOIDS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PRICES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||