| CAS
NO. |
489-84-9 |
|
| EINECS NO. |
207-701-2 |
| FORMULA |
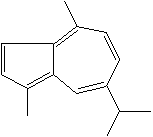
C15H18 |
| MOL
WT. |
198.31 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
|
|
TOXICITY
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
7-Isopropyl-1,4-dimethylazulene; |
| 1,4-Dimethyl-7-isopropylazulene;
Azulon; Guaiazlene; Azulen-Beris; Azulol; Azunol; Cuteazul; Eucazulen;
Gurjunazulen; Kessazulen; Purazulen; S-Guaiazulene; Silazulon; Uroazulen;
Vetivazulen; 1,4-Dimethyl-7-isopropylazulene; AZ-8; AZ-8 beris; Vaumigan; 3,8-Dimethyl-5-(2-propyl)azulene;
Guajazulene; Guiazulene; 1,4-Dimethyl-7-(1-methylethyl) Azulene; |
| SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
dark
blue seme-solid |
| MELTING POINT |
28 - 30
C |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
0.976 |
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
|
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
|
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
Health: 1 Flammability: 0 Reactivity: 0 |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
> 110 C |
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
|
Azulene is a main component of
chamomile extract which is used as a colouring
agent (azul means blue in Spanish) in cosmetics and ointments and used as a folk medicine to treat migraine, arthritis,
rheumatic diseases, and allergy. It
has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Examples of common substituted azulenes obtained naturally are vetivazulene
(4,8-dimethyl-2-isopropylazulene) from vetiver oil, and guaiazulene
(1,4-dimethyl-7-isopropylazulene) from constituent of guaiac wood oil.
Guaiazulene has been used as an antiulcer
drug. Various biological activities such as antiphlogistic,
antiallergic, bacteriostatic from azulen class compounds are expected. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
dark
blue semi-solid |
|
ASSAY |
98.5
- 101.0% |
|
MOISTURE |
0.1% max |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
20kgs
in Alu drum, 500gr in Alu drum |
| HAZARD CLASS |
Not
regulated |
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
Hazard
Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 22,
Safety Phrases: 24/25 |
|
PRICE
INFORMATION
|
|

|
