PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
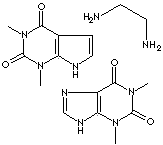
combination mixture of 3,7-dihydro-1,3-dimethyl-1H-Purine-2,6-dione with 1,2-ethanediamine (2:1); Phyllocontin;
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
white to slightly yellow powder or granular
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
APPLICATIONS
- Aminophylline: combination mixture of theophylline and ethylenediamine; used as a bronchodilator, diuretic agent and smooth muscle relaxant.
- Oxtriphylline: Choline theophyllinate (the choline salt of theophylline); administered orally.
- Theophylline Calcium Salicylate: an equimolar mixture of theophylline calcium and calcium salicylate; administered orally.
- Theophylline Sodium Glycinate: an equimolar mixture of theophylline sodium and glycine buffered with an additional mole of glycine and yielding 44.5 to 47.3 per cent anhydrous theophylline; administered orally.
- Theophylline Ephedrine: combination mixture of theophylline and ephedrine; to decongest the nasal allergic states, to relax bronchiolar muscles, to stimulate central nervous system in narcolepsy and in poisoning by central nervous system depressants; to prevent hypotension during spinal and infiltration anesthesia.
APPEARANCE
white to slightly yellow powder or granular
ASSAY
84.0-87.4% (Theophylline) + 13.5- 15.0% (Ethylenediamine)
IDENTIFICATION
Complies
SULFATED ASH
0.1% max
SOLUTION CLARITY
GY6 max
INDIVIDUAL IMPURITY
0.5% max
HEAVY METALS
20ppm max
25kgs in fiber drum
Caffeine is soluble in water and alcohol. It can be obtainable from coffee, tea, yerba mate, and guarana. It acts as an natural insecticide to protect plant themselves. Caffeine is used a central nervous system stimulant, diuretic and chemosterilant agent against stored grain pests. It is also used in the treatment of shock, asthma and heart disease. It is used for cardiac irritation, as a respiratory stimulant and diuretic in veterinary medicines. Theobromine has a weaker diuretic activity than theophylline and a different stimulant effects on the human body from caffeine. Theobromine is a mild and lasting stimulant with a mood improving effect, whereas caffeine is a powerful and immediate effect with an awareness increase. Caffeine was synthesized by methylation of theobromine but now recovered from the solvents used in the preparation of decaffeinated coffee. Theobromine was formerly used as a diuretic and in the treatment of angina pectoris and hypertension. Pentoxifylline, chemically 1-(5-oxohexyl)-3, 7-dimethylxanthine, is a drug which inhibits phosphodiesterase and affects blood rheology.