|
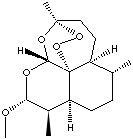
(+)-(3-alpha,5a-beta,6-beta,8a-beta,9-alpha,12-beta,12aR)-
decahydro- 10-methoxy- 3,6,9-trimethyl- 3,12-epoxy-
12H-pyrano(4,3-j)-1,2-benzodioxepin; Dihydroartemisinin,
12-beta-methyl ether; |
Artemether, isolated
from Chinese-Vietnamese plant Artemisia annua L., locally
called "qing hao", is used to treat fever and malaria. It is a white crystalline
powder with a bitter taste; practically insoluble in water, soluble in
chloroform, acetone, and alcohols. Its chemical designation is
(+)-(3-alpha,5a-beta,6-beta,8a-beta, 9-alpha,12-beta,12aR)- decahydro- 10-methoxy-
3,6,9-trimethyl- 3,12-epoxy- 12H-pyrano (4,3-j)-1,2-benzodioxepin.
Malaria is one of leading re-emerging infectious disease due to murative
malarial parasite developed resistance to chloroquine. Sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine
is an alternative can be used in the treatment of the disease resistant to
chloroquine, but resistance to sulfadoxine- pyrimethamine has been reported also
in some areas. Artemisinin is an alternative used in areas where the disease has
become highly resistant to sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine. Dihydroartemisinin, its
methyl ether (artemether), its ethyl ether (arteether) and its hemisuccinate ester (artesunate)
are known as
more effective than its parent material - artemisinin. But their activity decreases after one or two hours. For
simultaneous administration to counter the drawback,
combination
therapy of artemisinin along with lumefantrine,
mefloquine, amodiaquine, sulfadoxine,
and pyrimethamine
is useful. The term of artemotil refers to the pure beta-epimer
of arteether. Artemisinin is a
peroxide-bridged sesquiterpene lactone compound which has no N atom, unlike
quinine class anti-malarial drugs. The characteristic peroxide lactone structure is indispensable
for anti-malarial activity. This structure is also under the research for the
treatment of cancer. Examples of artemisinin molecules
include:
|
Product
|
CAS
RN
|
| Artemisinin |
63968-64-9 |
| Dihydroquinghaosu |
71939-50-9 |
| alpha-Artemether |
71939-51-0 |
| Artemether |
71963-77-4 |
| Deoxyartemisinin |
72826-63-2 |
| Arteether |
75887-54-6 |
| alpha-Propoxycarbonyl-dihydroartemisinine |
75918-39-7 |
| 3-Hydroxydeoxyartemisinin
|
82003-85-8 |
| Sodium artesunate |
82864-68-4 |
| Artesunate |
88495-63-0 |
| Deoxoartemisinin |
126189-95-5 |
| Artemisinin B |
145941-07-7 |
| Artemether-lumefantrine mixture | 141204-94-6 |
|