PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
Sodium Channel Modulator, Analgesic (non-narcotic), Anticonvulsant, Antimanic, Depressant, Peripheral Nervous System Agent, Psychotropic, Tranquilizing Agent
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY
Soluble in alcohol and in acetone
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbamazepine
http://www.nature.com/
Sodium channels can provide a route for a persistent influx of sodium ions into
neurons. Over the past decade, it has emerged that sustained sodium influx can,
in turn, trigger calcium ion influx, which produces axonal injury in
neuroinflammatory disorders such as multiple sclerosis (MS). The development of
sodium channel blockers as potential neuroprotectants in MS has proceeded
rapidly, and two clinical trials are currently ongoing. The route from the
laboratory to the clinic includes some complex turns, however, and a third trial
was recently put on hold because of new data that suggested that sodium channel
blockers might have multiple, complex actions. This article reviews the
development of the concept of sodium channel blockers as neuroprotectants in MS,
the path from laboratory to clinic, and the current status of research in this
area..........
http://web.me.com/
Sodium channel blockers are in wide spread use for the treatment
of pain, despite the fact that there actual mode of action is not fully
understood. It has been shown that the use of some of these blockers cause side
effects such as inhibiting calcium channels and thus neuronal signal
transmission, and in the case of Lamotrigine unexplained death. Currently there are three types of sodium channel blockers in use
for the treatment of neuropathic pain initially anticonvulsants as they reduce
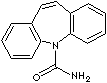
the synchronous firing of neurons. Carbamazepine (5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine-5-carboxamide) is used as the
‘first line’ treatment for the condition trigeminal neuralgia (TN), (3) a chroninc disorder of the trigeminal nerve, which is split into
3 divisions the Ophthalmic, Maxillary and Mandibular it causes debilitating
paroxysmal form of facial pain and can be present within one or all three of the
afor mentioned divisions of the trigeminal nerve. Carbamazepine is metabolised
to Carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide which displays a neuralgic effect, its mode of
action as an anti-convulsant is know but its mode of action for treatment of
neuropathic pain is unkown.........
APPEARANCE
IDENTIFICATION
passes Test
ASSAY
97.0-103.0% (on the dry basis)
LOSS ON DRYING
0.5% max
RELATED SUBSTANCES
0.2% max (Individual), 0.5% max (total)
HEAVY METALS
20ppm max
SULFATED ASH
0.1% max
ACIDITY
0.5ml max
MELTING POINT
189-193 C
PRICE INFORMATION