| CAS
NO. |
10380-28-6 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
233-841-9 |
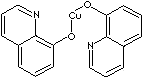
| FORMULA |
C18H12CuN2O2 |
| MOL
WT. |
351.85 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
|
|
TOXICITY
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
Bis(8-quinolinolato)copper;
Copper 8-hydroxyquinoline; |
| Quinolinol,
copper(II) chelate; Dokivin; Bioquin; Copper oxyquinolate;
Copper oxine; Cupric 8-hydroxyquinolate; Copper(II)-8-hydroxyquinoline;
Copper quinolate; Oxine-copper; Copper 8-hydroxyquinolinate;
Cupric 8-quinolinolate; Copper-oxinate; 8-Hydroxyquinoline
copper complex; Bis(8-oxyquinoline)
copper; Oxin-kupfer (German); Oxina-cobre (Spanish);
Oxine-cuivre (French); |
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
DISINFECTANTS
/
|
|
PHYSICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
yellow to
greenish powder |
| MELTING
POINT |
270
C (Decomposes) |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
Insoluble |
|
SOLVENT
SOLUBILITY
|
Insoluble in common organic solvents
(Slightly soluble in pyridine) |
| pH |
|
| VAPOR
DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
Health:
1; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 0 |
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
|
|
FLASH
POINT
|
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under normal conditions |
| GENERAL
DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
Disinfectant
is an agent applied to inanimate objects
to destroy, neutralize, or inhibit the
growth of disease-carrying microorganisms,
(whereas antiseptics are applied primarily
to living things). Heat and radiation
are also disinfectants. Common ingredients
of chemical disinfectant are:
- Mercuric
Chlorides
- Formaldehyde
- 8-Hydroxyquinoline
- Copper
Hydroxide
- Cresol
- Alcohols
(Ethyl Alcohol; Isopropyl Alcohol)
- Iodines
/ Iodophors
- Chlorine
releasing compounds
- Gluteraldehyde
- Phenolics
- Quaternary
Ammonium Compounds
Copper
quinolate is
used in formulating antiseptics, deodorants, antiperspirants
and fungicides. The biological property of copper compounds takes important role in as
fungicides in agriculture and biocides in antifouling paints for ships and wood
preservations. Very low level of copper is toxic to fungi and algae but the
levels for mammal is much higher. The copper ions inhibit the metabolism of the
fungus when they react with sulfur containing enzymes in the plant. Copper
compounds form a protective barrier on the plant surface and thereby prevent
fungi from entering the plant host. The fungicidal effect of copper compounds as
non-systemic fungicides are such as bordeaux mixture, cupric hydroxide, copper
arsenate, copper carbonate, cuprous oxide, copper-8-quinolinolate, copper
oleate, copper sulfate, or copper oxychloride. Another important biocide
application of copper compounds, such as copper sulfide is as an antifouling
agent in paints.
|
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
yellow to
greenish powder |
|
CONTENT
|
99.0%
min
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
25kgs
in fiber drum
|
| HAZARD
CLASS |
Not
regulated |
| UN
NO. |
|
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF QUINOLINE
|
| Quinoline,
1-azanaphthalene,
is an aromatic nitrogen compound
characterized by a double-ring structure contains a benzene fused to pyridine
at two adjacent carbon atoms.
(Pyridine is a ring structure compound of five carbon atoms with a nitrogen
atom). Quinoline itself
is the simplest member of the quinoline. It is a hygroscopic, yellowish oily liquid;
slightly soluble in water, soluble alcohol, ether, carbon disulfide
and readily in many organic solvents.
It can be obtained
by the distillation
of coal tar. Quinoline can be prepared from aniline with acrolein under heated
sulfuric acid (Skraup synthesis). Various quinoline
compounds can be prepared by Skraup synthesis series
of different oxidizing agents.
Isoquinoline differs from quinoline in
nitrogen position (at 2). Quinoline family compounds are widely used as a parent
compound to make drugs (especially anti-malarial medicines), fungicides,
biocides, alkaloids, dyes, rubber chemicals and flavoring agents. They have
antiseptic, antipyretic, and antiperiodic properties. They are also used as
catalyst, corrosion inhibitor, preservative, and as solvent for resins and
terpenes. They are used in transition-metal complex catalyst chemistry for
uniform polymerization and luminescence chemistry. They are used as antifoaming agent
in refinery field. Quinaldine,
2-methylquinoline,
is used as an
anti-malaria and preparing other anti-malaria drugs.
It is used in manufacturing oil soluble dyes, food
colorants, pharmaceuticals, pH indicators and other
organic compounds. Quinaldic Acid is
a carboxylic acid substituted quinoline at 2 position,
a catabolite of tryptophan (aromatic side chain amino
acid). Quinazoline,
diazanaphthalene at 1,3 positions,
is used
as a chemical intermediate for making medicines and
other organic compounds. It is a fundamental structure
in some antihypertensive
agents such as prazosin and doxazosin which are peripheral vasodilator.
Quinoxaline, diazanaphthalene
at 1,4 positions, is used as a chemical
intermediate for making fungicides and other organic compounds. |
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
| Hazard
Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 33, Safety Phrases: 24/25-37-45 |
PRICE INFORMATION
|
 |
