PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
146-56-5 (HCl)
5002-47-1(Decanoate)
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
FLASH POINT
APPLICATIONS
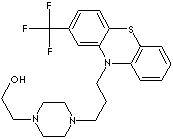
FLUPHENAZINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE
APPEARANCE
white crystalline powder
IDENTIFICATION
pass
ASSAY
98.5 - 101.5%
LOSS ON DRYING
1.0% max
SULFATED ASH
0.1% max
INDIVIDUAL IMPURITY
0.2% max (total 0.5% max)
HEAVY METALS
10ppm max
FLUPHENAZINE DECANOATE
APPEARANCE
pale yellow oily liquid or solid
IDENTIFICATION
complies
TEST A (IR-spectrum)
TEST B (thin-layer chromatography)
ASSAY
98.5 - 101.5%
LOSS ON DRYING
1.0% max
SULFATED ASH
0.1% max
HEAVY METALS
20ppm max
SHELF LIFE : 4 Years
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF ANTIPSYCHOTIC AGENTS
- Typical Antipsychotic
- Chlorpromazine (CAS #: 50-53-3, Phenothiazine with aliphatic side chain)
- Promazine (CAS #: 58-40-2, Phenothiazine with aliphatic side chain)
- Triflupromazine (CAS #: 146-54-3, Phenothiazine with aliphatic side chain)
- Methotrimeprazine (CAS #: 60-99-1, Phenothiazine with aliphatic side chain)
- Thioridazine (CAS #: 50-52-2, Phenothiazine with piperidine side chain)
- Mesoridazine (CAS #: 5588-33-0, Phenothiazine with piperidine side chain)
- Acetophenazine (CAS #:2751-68-0, Phenothiazine with piperazine side chain)
- Perphenazine (CAS #: 58-39-9, Phenothiazine with piperazine side chain)
- Trifluoperazine (CAS #: 117-89-5, Phenothiazine with piperazine side chain)
- Fluphenazine (CAS #: 69-23-8, Phenothiazine with piperazine side chain)
- Prochlorperazine (CAS #: 58-38-8, Phenothiazine with piperazine side chain)
- Chlorprothixene (CAS #: 113-59-7 Thioxanthene)
- Thiothixene (CAS #: 22189-31-7, Thioxanthene)
- Haloperidol (CAS #: 52-86-8, Phenylbutylpiperadine)
- Pimozide (CAS #: 2062-78-4, Phenylbutylpiperadine)
- Loxapine (CAS #: 1977-10-2, Dibenzoxazepine)
- Molindone (CAS #: 7416-34-4, Dihydroindolone)
- Atypical Antipsychotics
- Clozapine (CAS #: 5786-21-0, Dibenzoxazepine)
- Olanzapine (CAS #: 132539-06-1, Dibenzoxazepine)
- Quetiapine (CAS #: 111974-69-7, Dibenzoxazepine)
- Ziprasidone (CAS #: 138982-67-9, Benzisoxazole)
- Risperidone (CAS #: 106266-06-2, Benzisoxazole)
- Partial dopamine agonists
- Aripiprazole (CAS #: 129722-12-9, Dihydroquinolinone)
- Lithium carbonate