|
5-O-demethyl-22,23-dihydro-
avermectin
A; (10E,14E,16E,22Z)-(1R,4S,5'S,6S,6'R,8R,12S, 13S,20R,21R,24S)-6'-[(S)-sec-butyl]-21,24-dihydroxy-
5',11,13,22-tetramethyl-2-oxo-(3,7,19- trioxatetracyclo[15.6.1.14,8.020,24]
pentacosa-10,14,16,22- tetraene)-6-spiro-2'-(perhydro
pyran)-12-yl 2,6-dideoxy-4-O-(2,6- dideoxy-3-O-methyl-alpha-
L-arabino hexopyranosyl)- 3-O-methyl-alpha-L-arabino
hexopyranoside
+ (10E,14E,16E,22Z)-(1R,4S,5'S,6S,6'R,8R,12S, 13S,20R,21R,24S)- 21,24-dihydroxy-6'-isopropyl-5',11,13,22-
tetramethyl-2-oxo-(3,7,19-trioxa tetracyclo [15.6.1.14,8.020,24]
pentacosa-10,14,16,22-tetraene)-6- spiro-2'-(perhydropyran)-12-yl
2,6-dideoxy -4-O-(2,6-dideoxy-3-O-methyl-alpha- L-arabino hexopyranosyl)-3-O-methyl-
alpha-L-arabino hexopyranoside; |
|
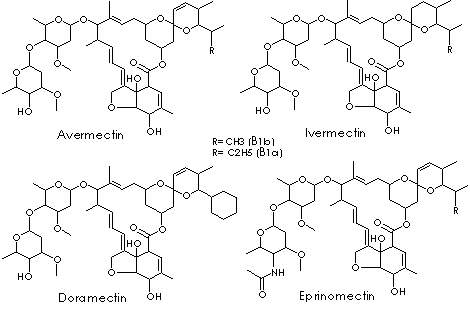
Avermectin: any of a group of pentacyclic sixteen-membered lactones derived from
the soil bacterium Streptomyces avermitilis. Avermectins are insecticidal or
anthelmintic compounds for domestic animals and sometimes humans. Abamectin is
the mixture of individual avermectin B1a(more than 90%) and avermectin B1b (not
more than 10%) components. A-series compounds are methoxylated at 5 position,
whereas the B-series have an underivatized hydroxyl group at the position. The
1-subset compound has an olefinic bond between C22 and C23; the 2-subset
possesses a hydroxyl group at position 23 due to the hydration of the double
bonds. They are considered to have very similar biological activities and
toxicological properties. Ivermectin is the most common avermectin. It is a
broad spectrum antiparasitic drug for oral administration. It is sometimes used
to treat human onchocerciasis. It is the mixture of 22,23-dihydro-avermectin B1a
(at least 90%) and 22,23-dihydro-avermectin B1b (less than 10 %),
differing by a single methylene group at 26 position. These are also
known as 5-O-demethyl-22,23-dihydro-avermectin A1a and 5-O-demethyl-22,23-dihydro-
avermectin
A1b
respectively. Ivermectin is a white to yellowish crystalline powder; nonhygroscopic;
melting point 155 C; insoluble in water; soluble in methanol and ethanol.
Doramectin has the closer structural similarity with abamectin than ivermectin.
There is a different substituent at the 25 position without the dihydro
modification at the 22,23 position. Doramectin is used as an endoparasitic agent
in non-lactating cattle. Eprinomectin is the amino-avermectin derived from avermectin B1 with modified
terminal oleandrose moiety. It is the mixture of
4"-epiacetylamino-4"-deoxy-avermectin B1a (> 90%) and B1b (< 10%).
Avermectin class acaricides or insecticides include:
- Abamectin
(CAS #: 71751-41-2)
- Avermectin B1a (CAS #:
65195-55-3)
- Avermectin B1b
(CAS #: 65195-56-4)
- Ivermectin (CAS #:
70288-86-7)
- 22,23-Dihydroxy-avermectin B1a (CAS #:
70161-11-4)
- 22,23-Dihydroxy-avermectin B1b (CAS #: 70209-81-3)
- Doramectin (117704-25-3)
- 25-cyclohexyl-5-O-demethyl-25-de(1-methylpropyl)-avermectin A1a
- Emamectin
- (4"R)-4"-deoxy-4"-(methylamino)-avermectin
B1a
(CAS #: 119791-41-2)
- (4"R)-4"-deoxy-4"-(methylamino)-avermectin B1b
(CAS #: 137335-79-6)
- Eprinomectin (CAS #:
123997-26-2)
- 4"-Deoxy-4"-epiacetylamino-avermectin B1a (CAS#: 133305-88-1)
- 4"-Deoxy-4"-epiacetylamino-avermectin B1b (CAS #: 133305-89-2)
- Selamectin (CAS #:
165108-07-6)
- (5Z,25S)-25-Cyclohexyl-4'-O-de(2,6-dideoxy-3-O-methyl-alpha-L-arabino-
hexopyranosyl)-5-demethoxy- 25-de(1-methylpropyl)-22,23-dihydro-
5-(hydroxyimino)-avermectin
A1a
|
