PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
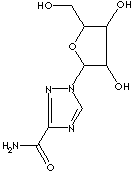
Antimetabolite is a chemical compound that closely resembles a metabolite in molecular structure, but can interfering with the normal reactions of the essential metabolite. It prevent the cell from the utilization of the genuine substance necessary to normal biochemical reactions. Chemically modified nucleotides substituted or attached by special chemical groups or elements are studied and used to inactivate the normal biological operation in the living organism and the function of important enzymes. Aminopterin (4-aminofolic acid) and methotrexate (mthylaminopterin) are antagonists of folic acid, and used in the treatment of some neoplastic diseases. Azathioprine and mercaptopurine are purine antagonists. 5-Fluorouracil and fluorodeoxyuridine are examples of pyrimidine antagonists; used as an antineoplastic and as a component of chemotherapy regimens. DNA synthesis inhibitors for antitumor effects include:
APPEARANCE
IDENTIFICATION
Complies
ASSAY (HPLC)
-33.5° ~ -37.0°
LOSS ON DRYING
0.5% max
10ppm max
RESIDUE ON IGNITION
0.1% max