| CAS
NO. |
13292-46-1 |
|
| EINECS NO. |
236-312-0 |
| FORMULA |
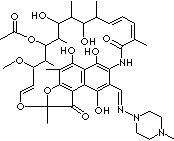
C43H58N4O12 |
| MOL
WT. |
822.95 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
3003.20 |
|
TOXICITY
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
Rifampicin; Rifaldazine;
Tubocin; |
| Rimycin; (2S,12Z,14E,16S,17S,18R,19R,20R,21S,22R,23S,24E)-1,2-Dihydro-5,6,9,17,19-
pentahydroxy-23-methoxy-2,4,12,16,18,20,22-heptamethyl-8-(4-methylpiperazin-
1-yliminomethyl)-1,11-dioxo-2,7- (epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]-trienimino)naphtho[2,1-b]
furan-21-yl
acetate; Rimactan; 3-(((4-Methyl-1-piperazinyl)imino)-methyl)
rifamycin; Sinerdol; |
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
Orange
to red-brown crystalline powder
|
| MELTING POINT |
183
- 188 C (Decomposes)
|
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
slightly
soluble
|
| pH |
4.5
- 6.5 |
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
|
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS
|
Rifamycin: a family of antibiotics divided into naphthalenic ansamycins.
Ansamycins are natural compounds characterized by a macrocyclic structure
consisting of an aromatic ring system connected to an aliphatic chain that forms
an amide linkage to the amino group of the aromatic moiety.
3-Amino-5-hydroxybenzoic acid (AHBA) is the start unit for the biosynthesis of
ansamycins. Based on the structure of the AHBA derived aromatic moiety, this
family of compounds can be further subdivided into a benzenic and a naphthalenic
sub-group. Geldanamycins, ansatrienins, and ansamitocins are the benzenic
ansamycins, which have been isolated from actinomycetes or higher plants. They
are mainly cytotoxic agents against eukaryotes. the naphthalenic ansamycins,
such as naphthomycins, streptovaricins, rifamycins, and tolypomycins, represent
antibacterial activity against gram-positive cocci, some gram-negative bacilli,
and Mycobacterium tuberculosis and certain other mycobacterial infections.
Rifamycins are biosynthesized by fermentation, and its biosynthesis involves the
assembly of a polyketide by addition of acetate and propionate chain extension
units to a unique start unit, AHBA. Further downstream processing of the
initially generated polyketide, proansamycin X, leads to the various chemically
modified rifamycins isolated from the fermentation. Rifamycins are used for the
treatment of tuberculosis, leprosy, gonorrhea, and biliary tract and respiratory
infections. They have been described as having in vitro activity against
Helicobacter pylori. The five components are designated A, B, C, D, and E;
rifamycin O, S, and SV are derivatives of the B component, and AG and X are
derivatives of the O component. Rifampicin is the international nonproprietary name for rifampin which is
derived from rifamycin SV; red-brown crystalline powder slightly soluble in
water at neutral pH, freely soluble in chloroform, soluble in ethyl acetate and
in methanol. The chemical designation is
5,6,9,17,19,21-hexahydroxy-23-methoxy-2,4,12,16,20,22-
heptamethyl-8- [N-(4-methyl-1- piperazinyl) formimidoyl]-2,7 - (epoxypentadeca
[1,11,13]trienimino) naphtho [2,1- b ] furan-1,11(2H)-dione 21-acetate. Rifampicin
acts by inhibiting the formation of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in susceptible
organisms by binding its beta subunit, thereby preventing the formation of
messenger RNA (mRNA) and the subsequent translation to proteins. Other rifamycins include followings:
- Rifabutin:
a semisynthetic antibiotic derivative from rifamycin S, used for the prevention
of disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex or tuberculosis; administered
orally.
- Rifamide: a derivative of rifamycin B;
used in the treatment of respiratory infections due to gram-positive cocci and
in biliary tract infections due to gram-negative and gram-positive
organisms.
- Rifapentine: similar antibiotic
to
rifampin but has a longer half-life than rifampin.
|
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
Orange
to red-brown crystalline powder
|
|
ASSAY |
97.0
- 103.0% |
|
RIFAMPIN QUINONE |
1.5%
max
|
|
INDIVIDUAL
IMPURITY
|
1.0%
max
|
|
TOTAL
IMPURITY
|
3.0%
max
|
|
HEAVY
METALS
|
10ppm
max
|
|
SULFATED
ASH
|
0.1%
max
|
|
LOSS
ON DRYING
|
1.0%
max
|
|
pH |
4.5 - 6.5 |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 22-36/37/38,
Safety Phrases: 26-36
PRICE
INFORMATION
 |
