PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
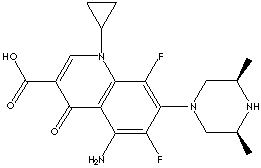
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
| Fluoroquinolone |
Substituent |
|
Substituted at N-1 |
|
|
Norfloxacin |
Ethyl |
|
Enoxacin |
Ethyl |
|
Lomefloxacin |
Ethyl |
|
Fleroxacin |
Fluoro ethyl |
|
Difloxacin |
Fluorophenyl |
|
Temafloxacin |
Difluorophenyl |
|
Trovafloxacin |
Difluorophenyl |
|
Amifloxacin |
Methyl amino |
|
Ciprofloxacin |
Cyclopropyl |
|
Grepafloxacin |
Cyclopropyl |
|
Alumofloxacin |
Cyclopropyl |
|
Gemifloxacin |
Cyclopropyl |
|
Moxifloxacin |
Cyclopropyl |
|
Ecenofloxacin |
Cyclopropyl |
|
Balofloxacin |
Cyclopropyl |
|
Substituted at C-5 |
|
|
Sparfloxacin |
Amine |
|
Grepafloxacin |
Methyl |
|
Substituted at C-7 |
|
|
Trovafloxacin |
Bicyclic |
|
Moxifloxacin |
Bicyclic |
|
Danafloxacin |
Bicyclic |
|
Garenoxacin |
Bicyclic |
|
Ciprofloxacin |
Piperazinyl |
|
Lomefloxacin |
Piperazinyl |
|
Norfloxacin |
Piperazinyl |
|
Fleroxacin |
Piperazinyl |
|
Ofloxacin |
Piperazinyl |
|
Sparfloxacin |
Piperazinyl |
|
Grepafloxacin |
Piperazinyl |
|
Gatafloxacin |
Piperazinyl |
|
Levofloxacin |
Piperazinyl |
|
Clinafloxacin |
Pyrrolidinyl |
|
Nadifloxacin |
Pyrrolidinyl |
|
Sitafloxacin |
Pyrrolidinyl |
|
Irloxacin |
Pyrryl |
|
Balofloxacin |
Piperidinyl |
|
Substituted at position 8 |
|
|
Sparfloxacin |
F |
|
Lomefloxacin |
F |
|
Fleroxacin |
F |
|
Ciprofloxacin |
CH2 |
|
Temafloxacin |
CH2 |
|
Pefloxacin |
CH2 |
|
Norfloxacin |
CH2 |
|
Grepafloxacin |
CH2 |
|
Clinafloxacin |
Cl |
|
Sitafloxacin |
Cl |
|
Enoxacin |
N |
|
Tosufloxacin |
N |
|
Gemifloxacin |
N |
|
Trovafloxacin |
N |
|
Ecenofloxacin |
N |
| Alatrofloxacin |
N |
|
Gatifloxacin |
Methoxy |
|
Pazufloxacin |
Methoxy |
|
Balofloxacin |
Methoxy |
|
Moxifloxacin |
Methoxy |
|
Garenoxacin |
Methoxy |
|
Tricyclic derivatives |
|
|
Abufloxacin |
|
|
Droxacin |
|
|
Flumequine |
|
|
Levofloxacin |
|
|
Marbofloxacin |
|
|
Miloxacin |
|
|
Ofloxacin |
|
|
Oxolinic acid |
|
|
Pazufloxacin |
|
|
Prulifloxacin |
|
|
Rufloxacin |
|
|
Verbafloxacin |
|
Sparfloxacin, the third generation drug of the quinolone antibiotics, is the virus reverse transcriptase inhibitor.
CLINICAL
APPLICATIONS;
-Uncomplicated urinary tract infections
-Complicated
urinary tract infections
-Pyelonephritis
-sexually transmitted
diseases
-prostatitis
-skin and tissue infections
-Urethral and
cervical gonococcal infections
-Acute exacerbations of chronic
bronchitis
-community-acquired pneumonia
APPEARANCE
98.0% min
USP 24
25kgs
in fiber drum
PRICE INFORMATION