PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
soluble
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
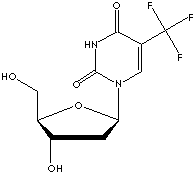
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS
- Urasil: a pyrimidine base
- Uridinea pyrimidine nucleoside
- Uridine Monophosphate (UMP, Uridylic acid): a nucleotide, the 5'-phosphate of uridine a component of ribonucleic acid.
- Uridine Diphosphate (UDP): a nucleotide, the 5'-pyrophosphate of uridine acting as the chief transferring coenzyme in carbohydrate metabolism acting as a carrier of hexoses, hexosamines, and hexuronic acids which are intermediates in the metabolism.
- Uridine Triphosphate (UTP): a nucleotide, the 5'-triphosphate of uridine acting as a precursor in the synthesis of ribonucleic acid and of UDP-linked intermediates.
- Deoxyuridine Monophosphate (dUMP): a nucleotide, the 5'-phosphate of deoxyuridine an intermediate in the synthesis of deoxythymidine triphosphate. (deoxy-, also called desoxy, is a prefix for the designation of compounds which contain one less atom of oxygen than the reference substance).
- Deoxyuridine Diphosphate (dUDP): a nucleotide, the 5'-phosphate of deoxyuridine an intermediate in the synthesis of deoxythymidine triphosphate.
- Deoxyuridine Triphosphate (dUTP): a nucleotide, the 5'-triphosphate of deoxyuridine an intermediate in the synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides.
Chemically modified nucleotides substituted or attached by special chemical groups or elements are studied and used to inactivate the normal biological operation in the living organism and the function of important enzymes.
Antimetabolite is a chemical compound that closely resembles a metabolite in molecular structure, but can interfering with the normal reactions of the essential metabolite. It prevent the cell from the utilization of the genuine substance necessary to normal biochemical reactions. Chemically modified nucleotides substituted or attached by special chemical groups or elements are studied and used to inactivate the normal biological operation in the living organism and the function of important enzymes. Aminopterin (4-aminofolic acid) and methotrexate (mthylaminopterin) are antagonists of folic acid, and used in the treatment of some neoplastic diseases. Azathioprine and mercaptopurine are purine antagonists. 5-Fluorouracil and fluorodeoxyuridine are examples of pyrimidine antagonists used as an antineoplastic and as a component of chemotherapy regimens. DNA synthesis inhibitors for antitumor effects include:
APPEARANCE
98.0 - 102.0%
Price: