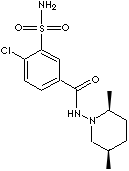
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
DERIVATION
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
- Potassium-sparing diuretics (Spironolactone, Eplerenone, Amiloride, Triamterene)
- Xanthine derivatives (Caffeine, Theophylline, Aminophylline, Theobromine, Meralluride, Pamabrom)
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (Acetazolamide, Dorzolamide, Furosemide)
- Loop diuretics (Furosemide, Bumetanide, Ethacrynic acid, Metolazone)
- Thiazide derivatives (Hydrochlorothiazide, Bendroflumethiazide)
- Osmotic diuretics (Sorbitol, Urea, Mannitol, Glucos, Isosorbide)
IDENTIFICATION
pass Test
ASSAY
MELTING POINT
230 - 232 C
LOSS ON DRYING
2.5% max
SULFATED ASH
0.2% max
HEAVY METALS
20ppm max