INDAPAMIDE
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Diuretics work by causing the kidneys to increase the
amount of salts such as potassium and sodium that are filtered out of the blood
and into the urine. When these salts are filtered out of the blood by the
kidneys, water is also drawn alongside. As diuretics increase the removal of
salts from the blood, they also cause more water to be drawn out of the blood
and into the urine.
Removing water from the blood decreases the volume of fluid
circulating through the blood vessels. This subsequently decreases the pressure
within the blood vessels. Diuretics are therefore used to lower high blood
pressure. Although indapamide is classed as a diuretic, its main
mechanism of lowering blood pressure is due to a direct action on the blood
vessels. Indapamide causes the blood vessels to widen, which reduces the
pressure inside the blood vessels. This helps to lower blood pressure........
(source:http://www.netdoctor.co.uk/)
Use: Management of mild to moderate hypertension; treatment of edema in congestive heart failure and nephrotic syndrome......... (source: http://www.merck.com/)
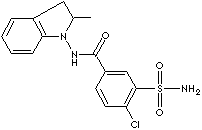
Indapamide hemihydrate is a nonthiazide indole derivative of chlorosulfonamide. It is a white crystalline lipophilic powder, soluble in methanol, ethanol, acetic acid and ethyl acetate, very slightly soluble in ether, chloroform and benzene and practically insoluble in water. Molecular weight: 374.85. Melting point: approximately 185°C. CAS Number: 26807-65-8. Indapamide is an oral antihypertensive agent. The mechanism whereby indapamide exerts its antihypertensive action has not been completely elucidated; both vascular and renal actions have been implicated......... (source: http://www.pbs.gov.au/)
Indapamide is an oral antihypertensive/diuretic. Its molecule contains both a polar sulfamoyl chlorobenzamide moiety and a lipid-soluble methylindoline moiety. It differs chemically from the thiazides in that it does not possess the thiazide ring system and contains only one sulfonamide group. The chemical name of indapamide is 4-Chloro- N-(2-methyl-1-indolinyl)-3-Sulfamoylbenzamide, and its molecular weight is 365.84. The compound is a weak acid, pKa=8.8, and is soluble in aqueous solutions of strong bases. It is a white to yellow-white crystalline (tetragonal) powder....... (source: http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/)APPEARANCE
ASSAY
98.5% min
160 - 162 C
LOSS ON DRYING
0.5% min