|
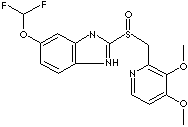
PANTOPRAZOLE SODIUM HYDRATE |
| 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-(((3,4-dimethoxy-2-pyridyl)methyl)sulfinyl)benzimidazole; Pantoprazolum; Pantoprazole sodium sesquihydrate, Pantozol sesquihydrate, Protonix sesquihydrate; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
102625-70-7 (parent), 138786-67-1 (sodium), 164579-32-2 (Sodium hydrate) |
|
EINECS RN |
|
|
FORMULA |
C16H14F2N3O4SNa·1/2H2O |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
405.35 (anhydrous basis) |
|
CHEMICAL FAMLY |
Benzimidazole |
|
CATEGORY |
Anti-ulcerative |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
white to off-white crystalline powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
139 - 140 C |
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Miscible (Very soluble in phosphate buffer at pH 7.4; practically insoluble in n-hexane) |
|
pH |
9.9 - 11 (2% solution) |
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBILITIES |
Oxidizing agents |
|
DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
|
| POLYMERIZATION | Has not been reported |
|
TOXICOLOGICAL NOTE |
Oral rat LD50: 747 mg/kg |
|
|
| SAFETY NOTES |
|
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
Harmful if swallowed. May cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. |
|
EYE |
May cause eye irritation |
|
SKIN |
May cause skin irritation. May be harmful if absorbed through skin. |
|
INGESTION |
Harmful if swallowed. |
|
INHALATION |
May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation. |
|
CHRONIC |
Possible hypersensitization. |
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
|
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
|
|
|
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS |
|
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pantoprazole Pantoprazole’s labeled indication is for the short-term treatment (no more than 16 weeks) of erosive esophagitis associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It may also show benefit for the maintenance treatment of erosive esophagitis, the treatment of duodenal and gastric ulcers, the prevention of gastro-duodenal damage in patients taking NSAIDs, and as adjunctive therapy with antibiotics for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Intravenous pantoprazole is indicated for the short-term treatment (7-10 days) of GERD, as an alternative for those patients who are unable to take the oral formulation. Other potential uses for intravenous pantoprazole include prevention of aspiration pneumonia in patients undergoing surgery, prevention of stress ulcers in intensive care patients, treatment of pyloric channel ulcers, and treatment of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. (http://www.hsc.wvu.edu/)Metabolism: Pantoprazole is extensively metabolized in the liver through the cytochrome P450 (CYP) system. Pantoprazole metabolism is independent of the route of administration (intravenous or oral). The main metabolic pathway is demethylation, by CYP2C19, with subsequent sulfation; other metabolic pathways include oxidation by CYP3A4. There is no evidence that any of the pantoprazole metabolites have significant pharmacologic activity. CYP2C19 displays a known genetic polymorphism due to its deficiency in some sub-populations (e.g. 3% of Caucasians and African-Americans and 17-23% of Asians). Although these sub-populations of slow pantoprazole metabolizers have elimination half-life values of 3.5 to 10.0 hours, they still have minimal accumulation (≤ 23%) with once daily dosing. (http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/) An analogue to omeprazole, used in the treatment of erosive esophagitis associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease, administered orally or intravenously, and of pathological hypersecretion associated with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome or other neoplastic conditions, administered intravenously. |
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
white to off-white crystalline powder |
|
ASSAY |
98.0 - 102.0% |
|
MELTING POINT |
139 - 140 C |
|
WATER |
4.0% - 6.0% |
|
RELATED SUBSTANCE |
1.0% max |
|
pH |
9.5 - 11 |
|
HEAVY METALS |
10ppm max |
|
|
| PACKING |
|
|
|
|
| PRICE |
|
|