| CAS
NO |
121-69-7 |
|
| EINECS NO. |
204-493-5 |
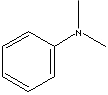
| FORMULA |
C6H5N(CH3)2 |
| MOL
WT. |
121.18 |
| H.S.
CODE |
2921.42
|
| TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: 1410 mg/kg |
| SYNONYMS |
Xylidine;
N,N-Dimethylbenzenamine;
Dimethylphylamine; |
|
DMA;
N,N-dimethylaniline;
(Dimethylamino)Benzene; N,N-Dimethylbenzenamine; ; Dwumetyloanilina (Polish); |
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
Pale Yellow to brown, oily liquid,
Amine-like odor |
| MELTING POINT |
2.45
C |
| BOILING
POINT |
193
- 195 C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
0.956
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
Negligible |
| pH |
weak base |
| VAPOR DENSITY |
4.17 |
| AUTOIGNITION
|
371
C
|
| NFPA
RATINGS
|
Health: 3 Flammability: 2
Reactivity: 0 |
| REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
1.5580 |
| FLASH
POINT |
63
|
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary
conditions |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
|
Aromatic amines are much weaker bases than the aliphatics. One of the most
important aromatic amines is aniline, a primary aromatic amine replacing one
hydrogen atom of a benzene molecule with an amino group. It is a pale brown
liquid at room temperature; boiling at 184 C, melting at -6 C; slightly soluble
in water and freely soluble in ether and alcohol. It causes serious industrial
poisoning. The substance may have effects on the blood, resulting in formation
of methaemoglobin. Repeated or prolonged exposures may be carcinogenic.
Commercial aniline is obtained from nitrobenzene which is prepared from benzene
with nitric acid by electrophilic substitution reaction or from chlorobenzene by
heating with ammonia in the presence of copper catalyst. It is also obtained as
a by-product of coal tar. In commerce the term of aniline oil blue refers to the
pure one while aniline oil red indicates a mixture of aniline and toluidines with
equimolecular weights. Aniline is the starting material in the dye
manufacturing industry. It forms aniline colors when combined with other
substances, particularly chlorine or chlorates. Aromatic amines are weaker bases
reacting with strong acids to form amides. Anilide is an amide derived from
aniline by substitution of an acyl group for the hydrogen of NH2. Acetanilide
is from acetic acid and aniline. Aniline is converted into
sulfanilic acid which is the parent compound of the sulfa drugs. Aniline is also
important in the manufacture of rubber-processing chemicals, explosives,
plastics, antioxidants and varnishes. Amines take part in many kinds of chemical
reactions and offer many industrial applications. N,N-Dimethylaniline is used as
an intermediate to manufacture dyes, vanillin, tetramethyldiaminobenzophenone
(white to greenish solid used as important intermediate for making dyes,
pigments and photosensitizers) and other organic products. It is also used as a
stabilizer for colorimetric peroxidase determination. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
Pale Yellow to
brown oily liquid, amine-like odor |
| PURITY |
99.5%
min
|
|
ORGANIC IMPURITY
|
0.4%
max
|
|
SETTING
POINT
|
2
C
|
|
MOISTURE
|
0.1%
max |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
180 Kg
in Drum |
| HAZARD CLASS |
6.1
(Packing group: II) |
| UN
NO. |
2253 |
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
N,N-Dimethylaniline decomposes
on heating or on burning producing highly toxic fumes of aniline,
nitrogen oxides. This compound is a weak base. It will reacts with
oxidants. Its color turns to darken on exposure to air and light.
|
|
PRICE
INFORMATION |
 |
