PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
EINECS NO.
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
Oral rat : LD50: 2250 mg/kg
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
MELTING POINT
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
Insoluble
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY
REFRACTIVE INDEX
115 C
APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
brown powder or flakes
MELTING POINT
80 - 100 C
ALKALINITY
500 - 590 ( mg HClO4/g)
HEAT LOSS
0.3% max
ASH
0.3% max
INSOLUBLE IN ETHANOL
0.1% max
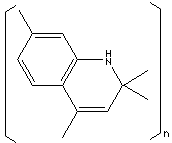
Quinoline, hygroscopic, yellowish oily liquid, is an aromatic nitrogen compound characterized by a solid-ring structure contains a benzene and a pyridine. (Pyridine is a ring structure compound of five carbon atoms with a nitrogen atom). These two rings are fused at two adjacent carbon atoms. Quinoline itself is the simplest member of the quinoline. It can be prepared by the distillation of coal tar or by synthesis from aniline. It is soluble in water as well as in alcohol, ether, and carbon disulfide. Isoquinoline differs from quinoline in nitrogen position. Quinoline family compounds are widely used as a parent compound to make drugs (especially anti-malarial medicines), fungicides, biocides, alkaloids, dyes, rubber chemicals and flavoring agents. They have antiseptic, antipyretic, and antiperiodic properties. They are also used as catalyst, corrosion inhibitor, preservative, and as solvent for resins and terpenes. They are used in transition-metal complex catalyst chemistry for uniform polymerization and luminescence chemistry.
PRICE