PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
70-55-3
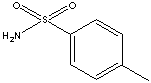
171.21
Oral rat LD50: 2330 mg/kg
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
white solid
136 - 140 C
221 C
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
Health: 1; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0
REFRACTIVE INDEX
202 C
APPLICATIONS
Amide is a group of organic chemicals with the general formula RCO-NH2 in which a carbon atom is attached to oxygen in solid bond and also attached to an hydroxyl group, where 'R' groups range from hydrogen to various linear and ring structures or a compound with a metal replacing hydrogen in ammonia such as sodium amide, NaNH2. Amides are divided into subclasses according to the number of substituents on nitrogen. The primary amide is formed from by replacement of the carboxylic hydroxyl group by the NH2, amino group. An example is acetamide (acetic acid + amide). Amide is obtained by reaction of an acid chloride, acid anhydride, or ester with an amine. Amides are named with adding '-ic acid' or '-oic acid' from the name of the parent carboxylic acid and replacing it with the suffix 'amide'. Amide can be formed from ammonia (NH3). The secondary and tertiary amides are the compounds which one or both hydrogens in primary amides are replaced by other groups. The names of secondary and tertiary amides are denoted by the replaced groups with the prefix capital N (meaning nitrogen) prior to the names of parent amides. Low molecular weight amides are soluble in water due to the formation of hydrogen bonds. primary amides have higher melting and boiling points than secondary and tertiary amides. Anilide is an amide derived from aniline by substitution of an acyl group for the hydrogen of NH2. Acetanilide is from acetic acid and aniline. Acetanilide is an odourless, white flake solid or crystalline powder (pure form); soluble in hot water alcohol, ether, chloroform, acetone, glycerol, and benzene;; melting point 114 C and boiling point 304 C; can undergo self-ignite at 545 C, but is otherwise stable under most conditions. Acetanilide which can be obtained by acetylation of aniline undergoes nitration at low temperature and yields highly the para-nitro products. Acetyl group can then be removed by acid-catalyzed hydrolysis to yield para-nitroaniline. Although the activating affection of the amino group can be reduced, the acetyl derivative remains an ortho/para-orientation and activating substituent. Examples of aromatic anilide are benzanilide, C6H5NHCOC6H5 or Carbanilide (N,N'-diphenylcarbamide). Some structural amides are;
- Acetamides
- Acrylamides
- Anilides
- Benzamides
- Naphthylamides
- Formamides
- Lactams
- Salicylamides
- Sulfonamides
- Thioamides
- Fatty amides
An amide is hydrolyzed to yield an amine and a carboxylic acid under strong acidic conditions. The reverse of this process resulting in the loss of water to link amino acids is wide in nature to form proteins, the principal constituents of the protoplasm of all cells. Sulfonamides are analogs of amides in which the atom attached to oxygen in solid bond is sulfur rather than carbon. Polyamide is a polymer containing repeated amide groups such as various kinds of nylon and polyacrylamides.
o-Toluenesulfonamide has been the parent material for the production of saccharin. In the phase of either solid or liquid, large amount of toluenesulfonamide class substances including the mixtures of N-ethyl-o/p-toluene sulfonamides, N-methyl-o/p-toluene sulfonamides and o/p-toluene sulfonamides are used as flow-promoting agents for paints, adhesives, nitrocellulose, coating materials and as plasticizers for polyamides and other thermosetting resins to increase flexibility. They promote the resistance to oils, greases, and solvents. They are used as antistatic agents and as gloss enhancers in plastic film preparations. They are used as basic material of electroplating solutions. Toluenesulfonamides, or derivatives thereof, are used as intermediate for a number of organic synthesis for the field of pharmaceuticals, pesticides, dyes, pigments, fluorescent brighteners, resins, and other organic target compound preparations. P-toluenesulphonamide is used as the precursor of nitrogen-containing crown ethers as designated for the 1,7-dioxa-4,10-diazacyclododecane ring system. Use of p-toluenesulphonamide as a derivative of ammonia activated to alkylation by alkyl halides is exemplified by the synthesis of N-tosyl-2,3-dihydroisoindole from o-xylylene dibromide. Toluenesulfonate esters are useful for the application as alkylating agents in organic synthesis.APPEARANCE
25 max
0.2% max
0.2% max
136 C
ISOMER IMPURITY
0.5% max
ASH
0.05% max
20ppm max
40ppm max
25kg in Bag