|
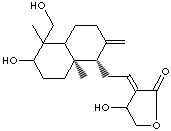
ANDROGRAPHOLIDE |
| 3-(2-(Decahydro-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenenaphthyl)ethylidene) dihydro-4-hydroxyfuran-2(3H)-one; Andrographis; (3E,4S)-3-(2-((1R,4aS,5R,6R,8aS)-6-hydroxy-5 -(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylidene-3,4,4a,6,7, 8-hexahydro-1H-naphthalen-1-yl) ethylidene)-4-hydroxyoxolan-2-one; |
|
|
| \PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
5508-58-7 |
|
EINECS RN |
226-852-5 |
|
FORMULA |
C20H30O5 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
350.45 |
|
CHEMICAL FAMILY |
Diterpine lactone |
| CATEGORIES |
Peripheral Nervous System agent |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
yellow to brown powder with bitter taste and characteristic odor |
|
MELTING POINT |
225 - 232 C |
|
BOILING POINT |
Decomposes |
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
|
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon oxides |
| POLYMERIZATION | Has not been reported |
|
TOXICOLOGICAL |
LD50 Intraperitoneal mouse: 11.460 mg/kg |
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
|
|
EYE |
May cause eye irritation. |
|
SKIN |
May cause skin irritation. May be harmful if absorbed through skin. |
|
INGESTION |
May cause irritation. May be harmful if swallowed. |
|
INHALATION |
May cause irritation. May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation. |
|
TARGET ORGANS |
|
|
CHRONIC |
|
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
|
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
20-24/25 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL INFORMATION |
|
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Andrographolide Andrographolide, the major phytoconstituent of Andrographis paniculata, was previously shown by us to have activity against breast cancer. This led to synthesis of new andrographolide analogues to find compounds with better activity than the parent compound. Selected benzylidene derivatives were investigated for their mechanisms of action by studying their effects on the cell cycle progression and cell death. Microculture tetrazolium, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) and sulphorhodamine B (SRB) assays were utilized in assessing the in vitro growth inhibition and cytotoxicity of compounds. Flow cytometry was used to analyse the cell cycle distribution of control and treated cells. (http://www.brjpharmacol.org/)Andrographolide, the active constituent, isolated from the plant Andrographis paniculata showed concentration dependent (1-100 microg/mL) activity against galactosamine (GALN 400 microg/mL) induced acute injury in isolated monkey hepatocytes, following 48 hours of the incubation at 370 C. The effect of andrographolide was measured on viability (trypan blue exclusion and oxygen uptake tests), biochemical marker enzymes - aspartate amino transaminase (AST), alanine amino transaminase (ALT) and alkaline phosphatase (AlP) and bile contents (bile salts and bile acids). It significantly increased the percent viability of cells and was capable of preserving 90-100% cell integrity. The cellular leakage of enzymes and bile contents following incubation with GALN was significantly modulated by andrographolide treatment. Its activity was found superior to that of silymarin, a standard hepatoprotective compound, tested simultaneously for comparison. The findings also emphasize the possible use of an in-vitro primary cell culture system as an alternative to in-vivo, in the early stage of drug discovery. (http://www.bepress.com/) Andrographolide is a chemical called a diterpine lactone found in the plant called Andrographis paniculata. This plant has been shown, scientifically, to have anti-inflammatory activity, which is an oriental traditional medicine used to treat inflammation. Injections of derivatives of andrographolide, called Lianbizhi, have been found to inhibit gastric, liver and lung cancers in living patients. Andrographolide, from Andrographis paniculata, is a chemical that has anti-inflammatory activity and has been shown by this study to be effective against several cancer cell lines. It was most effective against a type of prostate cancer cells in which it induced apoptosis and inhibited VEGF. (http://www.rainbowgrocery.org/) Pharmacologocal actions:
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
yellow to brown powder with bitter taste and characteristic odor |
| IDENTIFICATION |
pass |
|
ASSAY |
98.0% min (HPLC) |
| MELTING POINT | 225 - 232 C |
|
SULFATED ASH |
1.0% max |
| LOSS ON DRYING |
5.0%
max
|
| HEAVY METALS |
20ppm max |
| MICROBIOLOGICAL TESTS |
Total bacterial count:
1000CFU/g max Yeast and mold: 100CFU/g max Salmonella: negative E.Coli: negative Staphylococcus: negative |
|
|
| PACKING |
|
|
|
|
| PRICE |
|
|