|
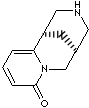
CYTISINE |
| 1,2,3,4,5,6-Hexahydro-1,5-methano-8H-pyrido(1,2-a)(1,5)diazocin-8-one; Baptitoxin; Baptitoxine; Citizin; Cystisine; Cytiton; Cytitone; Cytizin; Laburnin; Sophorin; Sophorine; Tabax; Tabex; Tsitizin; Ulexin; Ulexine; (1R,5S)-1,2,3,4,5,6-Hexahydro-1,5-Methano-8H-pyrido(1,2-a)(1,5)diazocin-8-one; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
485-35-8, 6047-01-4 (hydrochloride) |
|
EINECS RN |
207-616-0 |
|
FORMULA |
C11H14N2O |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
190.24 |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
yellowish powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
154 - 156 C |
|
BOILING POINT |
218 C at 2 mmHg |
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
|
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents. |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon oxides. nitrogen oxides, ammonia |
| POLYMERIZATION | Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2, Flammability: 1, Reactivity: 0 |
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
Toxic by ingestion, Irritant |
|
EYE |
Causes eye irritation. |
|
SKIN |
May be harmful if absorbed through skin. Causes skin irritation. |
|
INGESTION |
Toxic if swallowed. |
|
INHALATION |
May be harmful if inhaled. Causes respiratory tract irritation. |
|
CHRONIC |
|
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
2811 |
| HAZARD CLASS |
6.1 |
| PACKING GROUP |
III |
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
T |
|
RISK PHRASES |
25-36/37/38 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
26-28-36/37-45 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL INFORMATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Quinolizidine and isoquinoline alkaloids are a widely distributed, heterogeneous
group of alkaloids with members of each group having known toxicity to humans
and domestic animals. Cytisine, a tricyclic quinolizidine alkaloid found in Baptisia, Cytisus, Laburnum, and Sophora species, has nicotinelike effects on the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and the central nervous system (CNS). These plants may be smoked recreationally for their stimulant effects and mild hallucinogenic properties. Mescal bean may have been used by Native American peoples for ceremonial and medicinal purposes. Sophora root is used in traditional Chinese medicine where it is known as "Ku Shen" and is used to treat dysentery, scabies, itchy rashes including eczema, skin lesions, jaundice, edema, urinary dysfunction, and vaginal discharge. Lupinus species contain sparteine, a tetracyclic quinolizidine alkaloid, and lupinine, a bicyclic quinolizidine alkaloid. Lupinus species are broadly divided into bitter lupins that contain high levels of alkaloids in their seeds, and sweet lupins that contain lower levels of alkaloids and are cultivated for human consumption. Sweet lupins do contain sparteine and lupinine and must be soaked in water to prevent toxicity following ingestion. These two alkaloids are also found in other genera.(http://emedicine.medscape.com/) Cytisine is an attractive template for structural modification (Cassels et al., 2005). Substitution on the basic nitrogen atom generally seems to decrease its affinity and functional potency, probably to unacceptably low values. On the other hand, the introduction of substituents at carbon atoms 3 (also designated as 9) and 5 (or 11) is a fairly straightforward process, and the 3-bromo- and 3-iodo derivatives have subnanomolar affinities ( K i) for the epibatidine binding site in rat brain and are highly efficacious in different functional assays including dopamine release from striatal slices (Abin-Carriquiry et al., 2006). A number of 10(4)-substituted cytisine derivatives have been synthesized, and although none of them have higher nAChR affinities than cytisine, most of them have better α4β2 / α7 selectivities than cytisine and some surpass varenicline in this regard. Nevertheless, they seem to lack nAChR agonist activity, and have very low potency as nicotinic antagonists (Kozikowski et al., 2007). An additional drawback is the fact that they require fairly lengthy total syntheses, suggesting that any drug arising by this route would be much more expensive than one derived more directly from natural cytisine. (http://www.scitopics.com/) Nicotine receptor partial agonists may help people to stop smoking by a combination of maintaining moderate levels of dopamine to counteract withdrawal symptoms (acting as an agonist) and reducing smoking satisfaction (acting as an antagonist). Varenicline was developed as a nicotine receptor partial agonist from cytisine, a drug widely used in central and eastern Europe for smoking cessation. The first trial reports of varenicline were released in 2006, and further trials have now been published or are currently underway. (http://www.cochrane.org/) Drugs that bind to and activate nicotinic cholinergic receptor. Nicotinic agonists act at postganglionic nicotinic receptors, at neuroeffector junctions in the peripheral nervous system, and at nicotinic receptors in the central nervous system. Agents that function as neuromuscular depolarizing blocking agents are included here because they activate nicotinic receptors, although they are used clinically to block nicotinic transmission. (http://www.reference.md/) Nicotinic agonists
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
yellowish powder |
|
ASSAY |
98.0% min |
|
MELTING POINT |
154 - 156 C |
|
SPECIFIC ROTATION |
-119° ~ -121° |
|
|
| PRICE INFORMATION |
|
|