|
DORIPENEM |
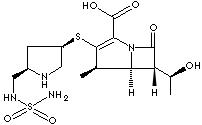
| Doribax; (+)-(4R,5S,6S)-6-((1R)-1-Hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-7-oxo-3-(((3S,5S)-5- ((sulfamoylamino)methyl) -3-pyrrolidinyl)thio)-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)hept-2-ene- 2-carboxylic acid; |
|
|
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
148016-81-3 |
|
EINECS RN |
|
|
FORMULA |
C15H24N4O6S2 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
420.50 |
|
CHEMICAL FAMLY |
beta-Lactam |
|
CATEGORY |
Carbapenem antibiotic |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
white to slightly yellow crystalline powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
|
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBILITIES |
Strong oxidizing agents |
|
DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon oxides, Nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides |
| POLYMERIZATION | Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
|
|
|
| SAFETY NOTES |
|
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
Harmful by inhalation and if swallowed. |
|
EYE |
May cause eye irritation |
|
SKIN |
May cause skin irritation. May be harmful if absorbed through skin. |
|
INGESTION |
May be harmful if swallowed. |
|
INHALATION |
May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation. |
|
CHRONIC |
|
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
|
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
|
|
|
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Doripenem Doripenem belongs to a class of antibacterial agents called carbapenems, which are useful in treating life-threatening infections caused by Gram-negative(1) and Gram-positive(2) bacteria. The data supporting the NDA showed doripenem was an effective treatment for hospital-acquired pneumonia. The data also demonstrated the effectiveness of doripenem against infections caused by Gram-negative bacteria, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacteriaceae, including strains of these bacteria that are resistant to other therapies. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is one of the leading causes of hospital-acquired infections and, because of increasing multi-drug resistance, treatment options are limited. In general, there are few antibiotics available or currently in development to treat the resistant infections - which can be potentially life-threatening - associated with these Gram-negative bacteria. (http://www.drugs.com/) Doripenem is a parenteral carbapenem with in vitro microbiological activity against a broad spectrum of clinically important Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens. It is approved for complicated intra-abdominal and complicated urinary tract infections (UTI) in the United States and in Europe, where it is also approved for nosocomial pneumonia. All carbapenems (except for ertapenem) have very similar pharmacokinetics, including half-life (1 hour), protein binding (2-20%), distribution properties (0.23-0.35 L/kg), and temporal plasma profiles. The value of dose individualization based on pharmacokinetic principles was recognized early in doripenem’s development and was integral to its clinical development. Using doripenem dosing regimens intended for clinical use, Bhavnani et al. developed a population pharmacokinetic model from limited intensively sampled data from a phase 1 study of 24 healthy volunteers with normal renal function http://aac.asm.org/) Doripenem, similar to other carbapenems, display bactericidal activity by inhibiting bacterial cell wall biosynthesis. More specifically, carbapenems bind to penicillin binding proteins (PBPs) and inhibit cross-linking of the peptidoglycan structure. The binding affinity of the carbapenems to PBPs can vary among bacterial species. In addition, individual carbapenem antibiotics (e.g., doripenem vs. imipenem) demonstrate varying affinities for PBPs and such differences may account for the more potent in vitro activity of doripenem against P. aeruginosa compared to imipenem. (http://www.pbm.va.gov/)
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
white to slightly yellow crystalline powder |
|
IDENTIFICATION |
pass Test I, II (HPLC, TLC) |
|
ASSAY |
98.5% min |
|
OPTICAL ROTATION |
+32° ~ +40° |
|
WATER |
7.0% |
|
RESIDUE ON IGNITION |
0.1% max |
|
HEAVY METALS |
10ppm max |
|
|
| PACKING |
|
|
|
|
| PRICE |
|
|