|
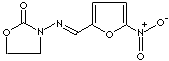
FURAZOLIDONE |
| 5-Nitro-N-(2-oxo-3-oxazolidinyl)-2-furanmethanimine; Giardil; Giarlam; Medaron; Furall; Furaxon; 3-(((5-Nitro-2-furanyl)methylene)amino)-2-oxazolidinone; Furoxane; Furoxon; Nifulidone; Nifuran; 3-((5-Ntrofurfurylidine)amino)-2-oxazolidinone; 3-((5-Nitrofurfurylidene)amino)-2-oxazolidone; 3-((5-Nitrofurylidene)amino)-2-oxazolidone; Bifuron; Corizium; Coryzium; Diafuron; 3-(5'-Nitrofurfuralamino)-2-oxazolidone; 5-Nitro-N-(2-oxo-3-oxazolidinyl)-2-furanmethanimine; Enterotoxon; Furaxone; Furazol; Furazolidine; Furazolidon; Furazolidona; Furazolidona; Furazolidone; Furazolidonum; Furazolum; Furazon; Furidon; Furovag; Furox; Furox; Furoxal; Furoxone; Furozolidine; N-(5-Nitro-2-furfurylidene)-3-amino-2-oxazolidone; Neftin; Nicolen; Nifurazolidonum; N-(5-Nitro-2-furfurylidene)-3-aminooxazolidine-2-one; Nitrofurazolidone; Nitrofurazolidonum; Nitrofuroxon; Optazol; Ortazol; Puradin; Roptazol; Sclaventerol; Tikofuran; Topazone; Trichofuron; Tricofuron; Tricoron; Trifurox; Viofuragyn; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
67-45-8; 8023-25-4; 8027-73-4 |
|
EINECS RN |
200-653-3 |
|
FORMULA |
C8H7N3O5 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
225.16 |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
yellowish crystalline powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
255 - 259 C |
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
40 mg/l |
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon oxides, nitrogen oxides |
| POLYMERIZATION | Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health:1 , Flammability:0 , Reactivity:0 |
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
Harmful, Possible risk of impaired fertility (male reproductive system). |
|
EYE |
May cause eye irritation. |
|
SKIN |
May be harmful if absorbed through skin. May cause skin irritation. |
|
INGESTION |
May be harmful if swallowed. |
|
INHALATION |
May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation. |
|
CHRONIC |
|
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
XN |
|
RISK PHRASES |
62 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
36 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL INFORMATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Chemistry - A synthetic nitrofuran-derivative antibacterial/antiprotozoal,
furazolidone occurs as a bitter-tasting, yellow, crystalline powder. It is
practically insoluble in water. Storage/Stability/Compatibility - Store protected from light in tight containers. Do not expose the suspension to excessive heat. Pharmacology - Furazolidone interferes with susceptible bacterial enzyme systems. Its mechanism against susceptible protozoa is not well determined. Furazolidone has activity against Giardia, Vibrio cholerae, Trichomonas, Coccidia and many strains of E. Coli, Enterobacter, Campylobacter, Salmonella and Shigella. Not all strains are sensitive, but resistance is usually limited and develops slowly. Furazolidone also inhibits monoamine oxidase. Uses/Indications - Furazolidone is usually a drug of second choice in small animals to treat enteric infections caused by the organisms listed above. Pharmacokinetics - Conflicting information on furazolidone’s absorption characteristics are published. As colored metabolites are found in the urine, it is clearly absorbed to some extent. Because furazolidone is used to treat enteric infections, absorption becomes important only when discussing adverse reactions and drug interaction issues. Furazolidone is reported to be distributed into the CSF. Absorbed furazolidone is rapidly metabolized in the liver and the majority of absorbed drug is eliminated in the urine. (http://www.elephantcare.org/) Furazolidone (FZD) is a synthetic nitrofuran derivative that is an antibacterial and antiprotozoal agent. FZD occurs as a yellow odorless crystalline powder with a bitter aftertaste. The drug is practically insoluble in water and alcohol. FZD is decomposed by alkali. The drug should be protected by light because it darkens on exposure to strong light and thus should be stored in light resistant containers. FZD is active against the protozoan Giardia lamblia (Giardia intestinalis) and against a range of bacteria in vitro including staphylococci, enterococci, Escherichia coli, Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., and Vibrio cholerae. FZD is bactericidal and appears to act by interfering with bacterial enzyme systems. Resistance is reported to be limited. It is used in the treatment of giardiasis, trichomoniasis, cholera and other vibrio infections1. It has been suggested for other bacterial gastrointestinal infections but antibacterial therapy with FZD is regarded as unnecessary in mild & self-limiting gastro-enteritis.1 However, FZD has been reported to possess anti-Helicobacter activity2 and to have some ulcer-healing properties. (http://www.trimed.com.au/) Pharmacological actioms of Furazolidone
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
yellowish crystalline powder |
|
ASSAY |
97.0 - 102.0% |
|
MELTING POINT |
255 - 259 C |
|
HEAVY METALS |
20ppm max |
|
RESIDUE ON IGNITION |
0.1% max |
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
0.5% max |
| pH |
5.5. - 7.0 |
|
|
| PACKING |
|
|
|
|
| PRICE INFORMATION |
|
|