|
POSACONAZOLE |
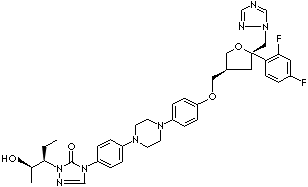
| 4-(p-(4-(p-(((3R,5R)-5-(2,4-Difluorophenyl)tetrahydro-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-3-furyl)methoxy) phenyl)-1- piperazinyl)phenyl)-1-((1S,2S)-1-ethyl-2-hydroxypropyl)-delta(2)-1,2,4-triazolin-5-one; Noxafil; 4-(4-(4-(4-(((3R,5R)-5-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-5-(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)oxolan-3-yl)methoxy)phenyl) piperazin-1-yl)phenyl)-2-((2S,3S)-2-hydroxypentan-3-yl)-1,2,4-triazol-3-one; Spriafil; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
171228-49-2 |
|
EINECS RN |
C37H42F2N8O4 |
|
FORMULA |
700.78 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Antifungal |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
white to off-white crystalline powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
168 - 172 C |
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
|
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents. |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon oxides. nitrogen oxides. |
| POLYMERIZATION | Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2 Flammability: 0 Reactivity: 0 |
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
Delayed target organ effects. Toxic by ingestion. Target Organs: Liver, Male reproductive system. |
|
EYE |
May cause eye irritation. |
|
SKIN |
May be harmful if absorbed through skin. May cause skin irritation. |
|
INGESTION |
Toxic if swallowed. |
|
INHALATION |
May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation. |
| MAIN RISKS AND TARGET ORGANS | |
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
2811 |
| HAZARD CLASS |
6.1 |
| PACKING GROUP |
III |
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
T |
|
RISK PHRASES |
25 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
36-45 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL INFORMATION | |
|
Posaconazole successful in treating fluconazole- and itraconazole-resistant
candidiasis
An open-label study of oral posaconazole has found that it safely and
effectively treats oropharyngeal and oesophageal candidiasis in people resistant
to fluconazole and/or itraconazole. The study was published in the February
15th issue of Clinical Infectious Diseases. Mucosal
candidiasis (‘thrush’) is an infection of the mouth and throat (oropharyngeal
candidiasis) and/or oesophagus (oesophageal candidiasis) by the fungi Candida
albicans and, more rarely, C. glabrata. Oral fluconazole is still the
mainstay of antifungal treatment for mucosal candidiasis (MC). After repeated
fluconazole treatment, 4 - 5% of people with advanced HIV (especially with CD4
cells counts below 100 cells/mm3) will develop fluconazole-resistant
MC. Alternative treatments include itraconazole and voriconazole (which may be
hampered by cross-resistance and drug interactions), and the more highly toxic
intravenous drugs amphotericin B and caspofungin.
(http://www.aidsmap.com/) Posaconazole belongs to the class of medications called antifungals. It is used to prevent certain serious fungal infections for people 13 years of age and older whose immune systems may be weakened by other medications or diseases. Posaconazole is also used for people 13 years of age and older to treat Candida infections of the mouth or throat (thrush). It is also used to treat Aspergillus infections that have not improved with other antifungal medications or when these medications have caused side effects. Posaconazole works by killing or stopping the growth of some types of fungi that can cause infections in people.(http://www.healthyontario.com/) Posaconazole is a member of the azole class of antifungals recently approved for the prophylaxis and treatment of invasive fungal infections. Posaconazole has a large volume of distribution and distributes well into tissues. Posaconazole-induced fungal killing is optimal when peak drug concentrations achieved are 2–10 times the organism’s minimum inhibitory concentration. Posaconazole demonstrates fungistatic activity against most species of Candida, Cryptococcus, and Trichosporon. In a direct comparison, posaconazole appeared 2–4 times more active than itraconazole against most pathogenic yeast species. Posaconazole also showed activity against Candida and Aspergillus isolates resistant to the other azoles and amphotericin B. Posaconazole has superior activity to the other azoles against Zygomycetes isolates. It has demonstrated activity equal or superior to other antifungal agents against almost all varieties of yeast and mold. The most common treatment-related adverse events associated with posaconazole are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, rash, hypokalemia, thrombocytopenia, and abnormal liver function test values. Significant drug interactions include cimetidine, rifabutin, and phenytoin, for which concomitant use should be avoided, as well as cyclosporine, tacrolimus, and midazolam, for which dosage reductions are recommended. (http://www.ajhp.org/)Pharmacological Actions
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
white to off-white crystalline powder |
| PURITY |
98.0% min |
| MELTING POINT |
168 - 172 C |
|
|
| PRICE INFORMATION |
|
|