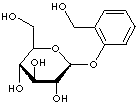
|
SALICIN |
| 2-(Hydroxymethyl)phenyl beta-D-glucopyranoside; o-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol o-glucoside; Salicine; Salicoside; Salicyl alcohol glucoside; Saligenin beta-D-glucopyranoside; Saligenin-beta-D-glucopyranoside; o-(Hydroxymethyl)phenyl beta-D-glucopyranoside; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
138-52-3 |
|
EINECS RN |
205-331-6 |
|
FORMULA |
C13H18O7 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
286.28 |
|
CHEMICAL FAMILY |
Monosaccharide |
| CATEGORIES | Extractives and their physically modified derivatives |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
white crystals with characteristic odor |
|
MELTING POINT |
197 - 200 C |
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Soluble (Soluble in alkalies, pyridine) |
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon oxides |
| POLYMERIZATION | |
|
TOXICOLOGICAL |
|
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
May cause an allergic skin reaction. |
|
EYE |
Causes eye irritation. |
|
SKIN |
Harmful if absorbed through skin. Causes skin irritation. |
|
INGESTION |
Harmful if swallowed. |
|
INHALATION |
Harmful if inhaled. Causes respiratory tract irritation. |
|
TARGET ORGANS |
|
|
CHRONIC |
|
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
XI |
|
RISK PHRASES |
43 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
36/37 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL INFORMATION |
|
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salicin Salicinum, Salicin, C13H18O7,- is a neutral principle obtained from several species of Salix (willow) and Populus (poplar), also found in Gaultheria procumbens (wintergreen) and in Betula lenta (sweet birch), the volatile oils of which consist almost entirely of methyl salicylate. It occurs in white, silky, crystalline needles; soluble in 28 of water and in 30 of alcohol. Acidum Salicylicum, Salicylic Acid, HC7H5O3,- is an organic acid, existing in various plants, but most largely prepared synthetically from carbolic acid. Occurs in fine, prismatic needles or a crystalline powder; soluble in about 450 of water and in 2 1/2 of alcohol, but readily soluble in water containing 8 per cent. of borax or 10 of sodium phosphate. Salicylic Acid is a derivative of Salicin, probably by solid oxidation; but may also be considered as a substitution-derivative of Benzene, formed by replacing 2 atoms of its hydrogen, the one by hydroxyl, and the other by carboxyl. It is obtained, therefore, either synthetically by combining the elements of Carbolic Acid with those of Carbonic Acid, and subsequent purification,-or from natural Salicylates as the oils of wintergreen and sweet birch,- or from Salicin, by heating with caustic potash and treating the mass with hydrochloric acid. The acid prepared from natural sources is purer and more efficient than that prepared artificially, and will often be tolerated by a patient who cannot bear the latter. (http://www.henriettesherbal.com/) Herbalists have used extract of the bark of the willow (Salix spp.) to treat a variety of complaints. The name salicin was given to the basic compound with a molecule incorporating 2 rings. One of these rings is equivalent to a glucose molecule, so this called a glycoside. A similar substance is produced by other plants, such as the Meadowsweet flower. By removing the glucose unit from salicin, a molecule with a single ring structure was obtained: salicylic acid (ortho hydroxy benzoic acid). This substance was not very effective as a drug. Interestingly, the name aspirin - registered in 1899 - results from a for acetyl + spirin, meaning a substance obtained from Spiraea, which is the name which used to be given to the plant Meadowsweet. (http://www.biotopics.co.uk/)The bark of white willow contains salicin, which is a substance similar to aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). Salicin may be the chemical involved in the pain-reliving and anti-inflammatory effects of the white willow herb. In fact, in the 1800s, salicin was used to develop aspirin. White willow bark extract does appear to have some analgesic properties. (http://www.raysahelian.com/) Pharmacological actions:
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
white powders with characteristic odor |
| SALICIN |
98.0% |
|
MELTING POINT |
197 - 200 C |
|
HEAVY METALS |
10ppm max |
| ARSENIC |
1ppm max |
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
1.0% max |
|
ASH |
0.5% max |
| MICROBIOLOGICAL TESTS |
Total plate count:
1000CFU/g mac Yeast and mold: 100CFU/g Salmonella: negative E.Coli: negative Staphylococcus: negative P.Aeruginosa: negative |
|
|
| PACKING |
|
|
|
|
| PRICE |
|
|