|
SILYMARIN |
| Flavobion; Legalon; Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) Extract; Milk thistle; Silybum marianum; Wild Artichoke; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
65666-07-1 |
|
EINECS RN |
245-302-5 |
|
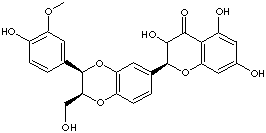
FORMULA |
C25H22O10 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
482.44 |
|
CHEMICAL FAMILY |
Flavonoid |
| CATEGORIES | Antioxidant |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
yellow powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
230 - 233 C |
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
|
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
|
| POLYMERIZATION | Has not been reported |
|
TOXICOLOGICAL |
|
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
|
|
EYE |
May cause eye irritation. In case of eye contact, flush eyes with water as a precaution. |
|
SKIN |
May be harmful if absorbed through skin. In case of skin contact, wash off with soap and plenty of water. |
|
INGESTION |
May be harmful if swallowed. Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Rinse mouth with water. |
|
INHALATION |
May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation. If breathed in, move person into fresh air. If not breathing give artificial respiration. |
|
TARGET ORGANS |
Liver |
|
CHRONIC |
|
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
XI |
|
RISK PHRASES |
36/37/38 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
26-37/39 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL INFORMATION |
|
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Silymarin Silymarin is derived from Milk Thistle (seed extract from the flower of silymarin plant). The Milk thistle herb is a flowering plant of Silybum Adans genus, a member of the daisy family (Asteraceae). It grows mainly in North Africa, the Mediterranean region and the Middle East (now also grown in the U.S.) but is marketed and is widely available in the Philippines as a herbal liver supplement (silymarin capsules, trademark: Liveraide). Silymarin and milk thistle are frequently used interchangeably. Laboratory experiments on animals (rats, baboons, dogs) shows that silymarin works by modifying hepatic cell membranes in a way that prevents liver toxins from entering the interior of the cells. The toxins that may damage the liver are expelled through the kidneys instead. Silymarin is a polyphenolic flavanoid consisting of three chemicals: silybin, silicristin and silidianin which are antioxidants that neutralizes and breaks down free radicals. When there is an existing liver damage, research shows that silymarin may help repair the damage and help regenerate new liver cells but is unlikely to help in the late stages of liver cirrhosis. Many studies have been published on the health benefits of milk thistle and silymarin on humans but many are inconclusive or poorly done. Further studies are needed to fully appreciate the health benefits of silymarin on humans. However, anecdotal data suggests that it helps alleviate liver diseases and other aliments. http://www.philippineherbalmedicine.org/silymarin_milk-thistle.htm Milk thistle is a flower, more specifically a member of the aster family. Its seeds and roots have been used for an assortment of medical purposes for thousands of years. Three biochemicals of interest have been isolated from the milk thistle: silychristine, silydianin, and silybin, which is also called “silybinin” and is considered the most powerful of them all. The mixture of these three substances is called “silymarin.” Silymarin has been traditionally used in the treatment of liver disease and, while it has recently been advocated for use in pets, most scientific information available concerns human use. The biological mechanism of action is yet unknown but several theories exist:
Silymarin, the active ingredient in Milk Thistle, exerts numerous effects of interest to Dermatologists. Although it has been primarily know as a herb for the liver, it exerts a number of important effects in the skin. It not only demonstrates anti-carcinogenic and anti-pruritic effects on the skin, but also holds great interest as a potential agent to reduce or ameliorate the liver toxicity caused by certain drugs employed by dermatologists. (http://dermatology.cdlib.org/)
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
yellow powder |
| IDENTIFICATION |
pass (TLC) |
|
CONTENT |
80.0% min (Silymarin) |
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
5.0% max |
| HEAVY METALS |
10ppm
max
|
| IRON |
5ppm max |
| SULFATED ASH |
1.0% max |
| PARTICLE SIZE |
100 mesh (95%) |
| MICROBIOLOGICAL TESTS |
Total bacterial count:
1000CFU/g max Yeast and mold: 100CFU/g max Salmonella: negative E.Coli: negative Staphylococcus: negative |
|
|
| PACKING |
|
|
|
|
| PRICE INFORMATION |
|
|